Why Cadaver Labs Remain Essential in Modern Medical Education
A cadaver-lab is a specialized facility where medical students and healthcare professionals study human anatomy through hands-on dissection of donated human bodies. These labs serve as the cornerstone of medical education, bridging theoretical knowledge with practical skills development.
Key Components of a Cadaver Lab:
- Preserved human specimens - Bodies donated to science for educational purposes
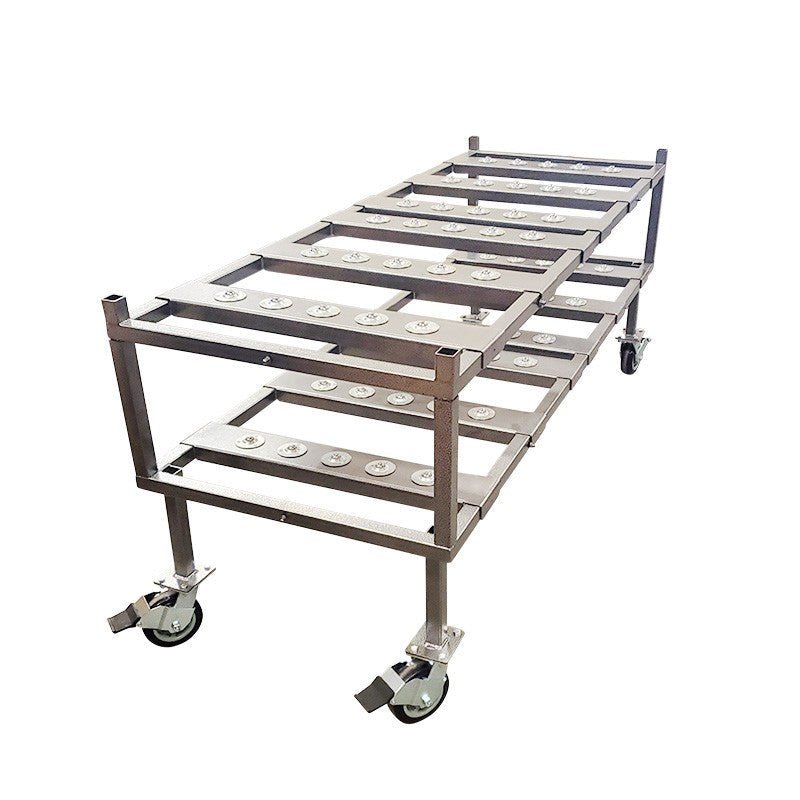
- Dissection tables and tools - Specialized equipment for anatomical exploration
- Safety protocols - PPE requirements, ventilation systems, and chemical handling
- Educational structure - Guided curriculum covering organ systems and pathology
- Ethical framework - Donor respect ceremonies and professional conduct standards
Research shows that 87% of medical students report that cadaver labs significantly improve their learning retention. Unlike digital simulations, cadaver labs provide irreplaceable tactile feedback, reveal natural anatomical variations, and foster the empathy essential for patient care.
Modern applications include surgical skills training, medical device testing, and specialized procedures like orthopedic joint replacement and facial anatomy for aesthetic medicine. With approximately 20,000 Americans donating their bodies to science each year, these facilities continue to play a vital role in advancing medical knowledge and patient care.
Why This Guide Matters
This comprehensive guide serves medical students preparing for their first anatomy course, healthcare professionals seeking continuing education, and institutions planning cadaver lab facilities. We'll explore the historical evolution of human dissection, modern innovations, and specialized applications across medical disciplines.
The Evolution of Human Dissection
The story of human dissection begins in ancient Greece, where physicians like Herophilus and Erasistratus first systematically studied human anatomy around 300 BCE in Alexandria, laying the groundwork for modern medicine.
For over a thousand years, cultural and religious taboos essentially shut down human dissection. Medieval physicians had to make do with animal dissection and ancient texts, leading to significant misunderstandings about human anatomy.
The 15th century marked a dramatic turning point. European universities, led by the University of Bologna, began hosting regular cadaveric dissections as theatrical events in grand anatomical theaters, complete with audiences who came for both education and entertainment.
Andreas Vesalius changed everything during the Renaissance. In 1543, he published "De Humani Corporis Fabrica," correcting centuries of anatomical errors. More importantly, Vesalius performed dissections himself, establishing the foundation for modern anatomical education where direct observation trumps textbook assumptions.
The 18th and 19th centuries brought both progress and unsavory practices. Medical schools needed more bodies than the legal system could provide, leading to the infamous "body-snatching" era. Grave robbers would dig up fresh graves to supply medical schools with specimens, leading to public outrage and eventually the Burke and Hare murders in Edinburgh.
The Anatomy Act of 1832 in Britain, followed by similar legislation worldwide, established legal frameworks for obtaining bodies for medical education. These laws evolved into today's voluntary donation systems, changing what once inspired fear into the beautiful concept of "silent teachers" - generous individuals who donate their bodies to help train future doctors.
This historical journey reflects humanity's growing understanding that there's no substitute for working with actual human anatomy, explaining why the modern cadaver-lab remains vital in training healthcare professionals.
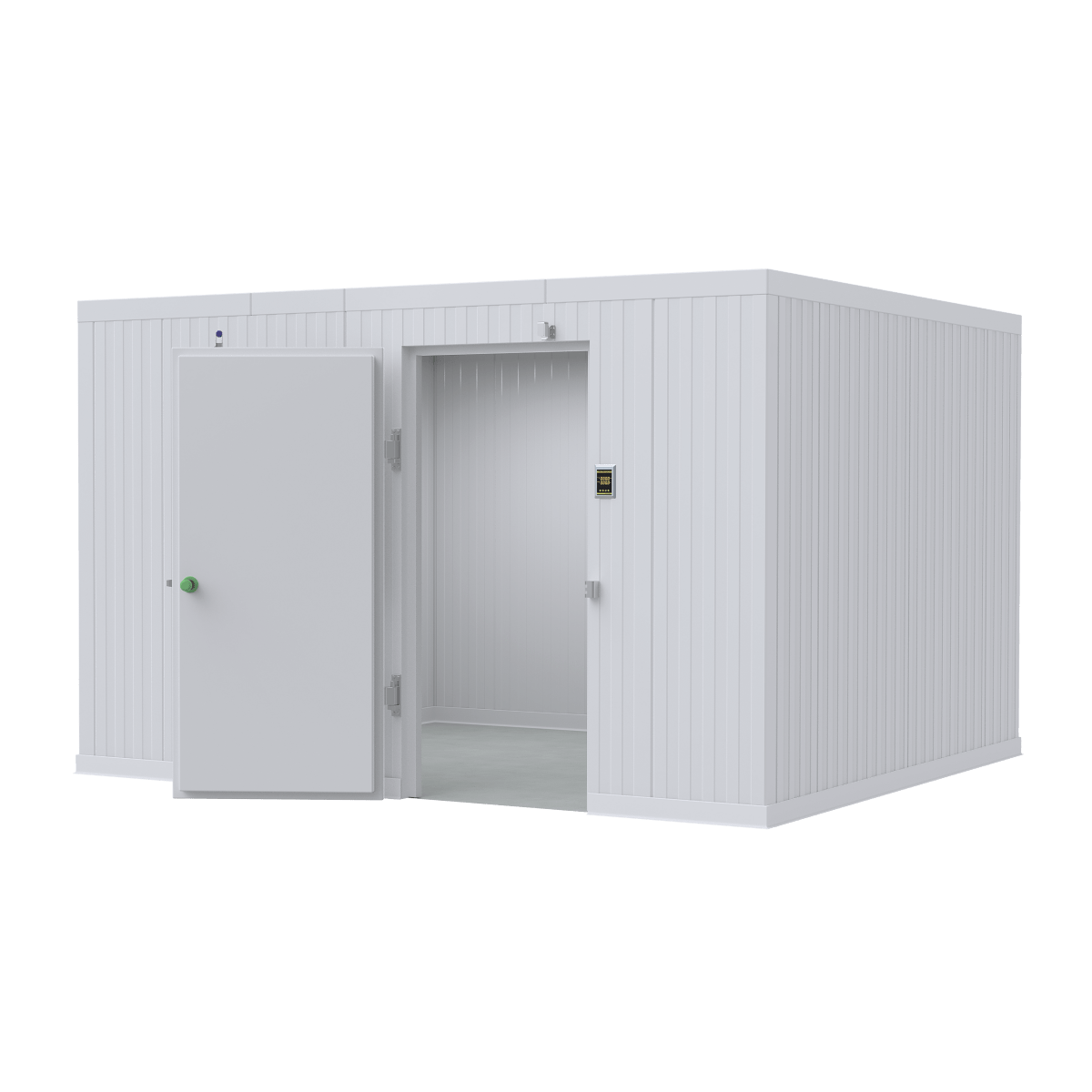
Inside a Modern Cadaver-Lab: Purpose, Setup & Safety
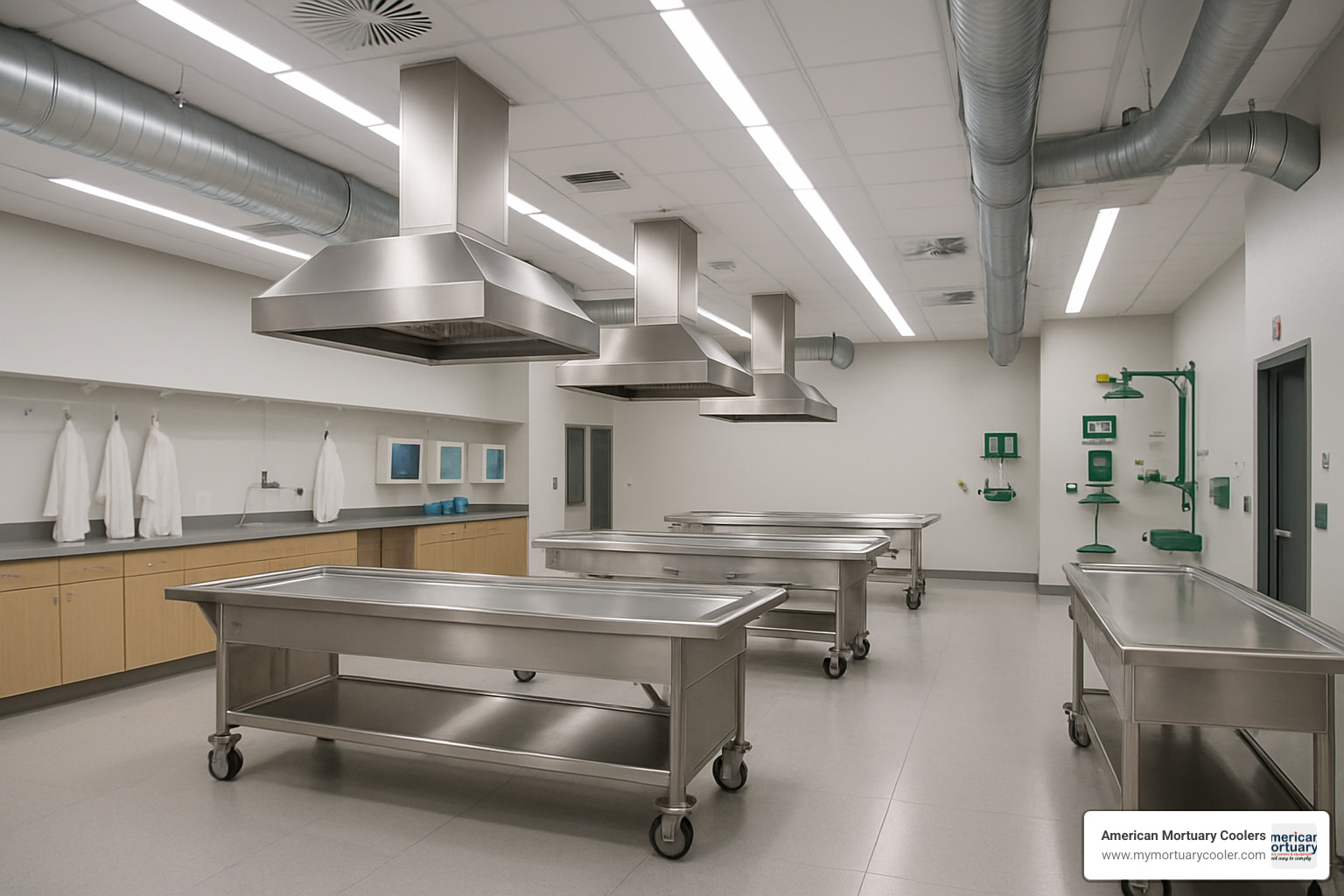
Modern cadaver-lab facilities are bright, well-ventilated spaces that feel more like high-tech surgical suites than traditional anatomy rooms. These labs serve multiple roles: giving students tactile experience with real human tissue, allowing surgeons to practice new techniques, enabling researchers to test medical devices, and helping pathologists study diseased tissues.
The physical setup includes specialized dissection tables with built-in drainage systems, temperature control, and sophisticated ventilation systems that continuously circulate fresh air while managing chemical preservatives.
Essential protective equipment includes nitrile gloves, safety glasses, full-coverage lab coats, closed-toe shoes with chemical-resistant soles, hair restraints, and face masks for protection from preservative vapors.
Preservation methods have evolved dramatically. Traditional formaldehyde-based preservation creates stiff, discolored tissues, while newer techniques like Thiel embalming preserve natural texture and flexibility, creating more realistic learning experiences.
Core Benefits of the cadaver-lab Experience
Research consistently shows that students who learn through hands-on dissection retain information better than those using only digital alternatives. The 87% of medical students who report improved learning retention experience genuine educational advantages through "real tissue feedback" - feeling the difference between thin atrial walls and thick ventricular walls, seeing how blood vessels actually branch and connect.
Scientific research on anatomy retention confirms that hands-on dissection significantly improves knowledge retention compared to digital alternatives. The three-dimensional nature of cadaveric study helps students understand spatial relationships impossible to convey through textbooks or screens.
Cadaver-lab experiences also reduce student anxiety about clinical practice and foster empathy, respect for human life, and deeper understanding of mortality - qualities essential for compassionate patient care.
Developing Surgical & Clinical Skills
Specialized applications extend beyond basic anatomy. Orthopedic programs use cadaveric specimens for joint replacement procedures and fracture repair. The minimally invasive surgery field, valued at $34.0 billion in 2024, depends heavily on cadaver lab training for laparoscopic and robotic surgery techniques.
Perfused cadavers with restored blood circulation allow practitioners to observe bleeding and practice controlling hemorrhage. While expensive at approximately €2,000 per training day, they provide unparalleled surgical training realism.
Facial anatomy cadaver labs have become essential for aesthetic medicine practitioners performing dermal filler injections and laser treatments, helping them understand tissue layers and vascular patterns crucial for safe treatment outcomes.
Safety & Risk Management
Comprehensive safety protocols protect participants and specimens. Chemical exposure management is the top priority, with proper ventilation systems and regular exposure monitoring. Sharps safety protocols prevent injuries, while infection control measures maintain professional standards through regular hand hygiene and workspace disinfection.
Cadaver Labs vs. Simulation & Virtual Anatomy
Modern medical education features exciting technologies like virtual reality systems, augmented reality applications, and high-fidelity patient simulators. The Anatomage Table lets students explore 3D anatomy without formaldehyde concerns, while sophisticated manikins can change vital signs and respond to treatments for unlimited practice.
| Aspect | Cadaver Labs | Simulation Labs |
|---|---|---|
| Anatomical Realism | Authentic human tissue and variations | Standardized synthetic models |
| Tactile Feedback | Natural tissue response | Limited tactile simulation |
| Repeatability | Limited by specimen degradation | Unlimited repetition |
| Cost | High specimen and facility costs | High initial equipment investment |
| Emotional Impact | Profound respect and empathy development | Minimal emotional engagement |
| Safety | Chemical exposure risks | Minimal safety concerns |
The cadaver-lab experience provides profound emotional and professional development that technology struggles to replicate. Scientific research on simulation anxiety shows that while simulation reduces performance anxiety, it may not fully prepare students for the emotional realities of patient care.
When to Choose Each Modality
Smart medical schools use the right tool for the right job. Pre-clinical learning works well with digital anatomy platforms, while advanced procedural training, especially surgical specialties, requires the authentic tactile feedback of human specimens.
Hybrid educational models are becoming standard - students start with digital anatomy study, progress to simulation for basic skills, then move to cadaver lab experience for advanced learning. This progressive approach maximizes benefits while keeping costs manageable.
As one educator noted, "Cadaver labs inspire empathy and respect for human life in a way simulations cannot" - ensuring their continued importance in medical training.
Ethics, Body Donation & Professionalism
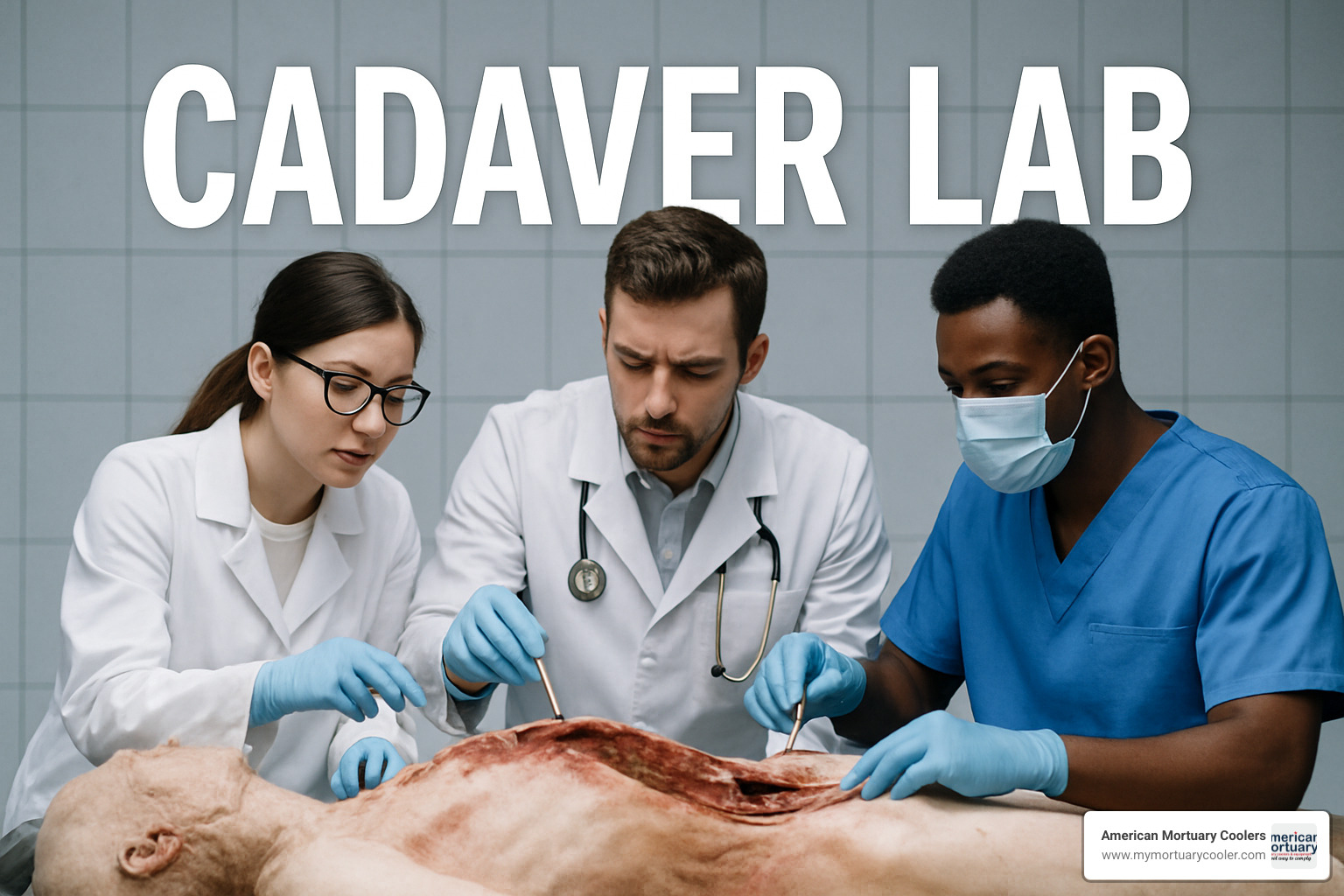
Every body in a cadaver-lab represents someone who made a profound choice to become a teacher after death. This extraordinary gift forms the ethical heart of medical education and deserves our deepest respect.
Informed consent involves comprehensive discussions about how bodies will be used, duration of the process, and final disposition. The regulatory framework through organizations like the American Association of Tissue Banks sets strict standards for donor screening, facility requirements, and respectful handling.
Most institutions hold donor ceremonies bringing together students, families, and faculty to honor these silent teachers. Anonymity protects both donors and students by maintaining professional boundaries, while respect rituals vary but share common threads of acknowledgment and gratitude.
More info about body donation explains how families steer this meaningful decision.
The Donation Journey
The path from donation decision to education involves careful steps honoring both donor wishes and educational needs. Pre-registration allows donors to discuss choices with family and specify restrictions. Donor screening evaluates safety for educational use, while transportation and preservation happen quickly to maintain tissue quality.
Preparation takes several weeks using formaldehyde-based solutions or newer methods. Allocation to programs considers donor preferences and educational needs. Final disposition completes the journey with memorial services and appropriate burial or cremation.
Fostering Empathy Through Dissection
Emotional preparation addresses student anxiety about encountering death. Coping strategies include peer support groups, counseling services, and faculty mentorship. The "first patient" concept transforms the experience from studying specimens to learning from teachers who carry the same ethical obligations as any patient encounter.
Professional conduct codes establish behavioral expectations, while reflective writing helps students process their journey and develop empathy. The long-term impact shapes entire medical careers, preparing doctors for difficult conversations and end-of-life care decisions.
Innovations & Specialized Applications
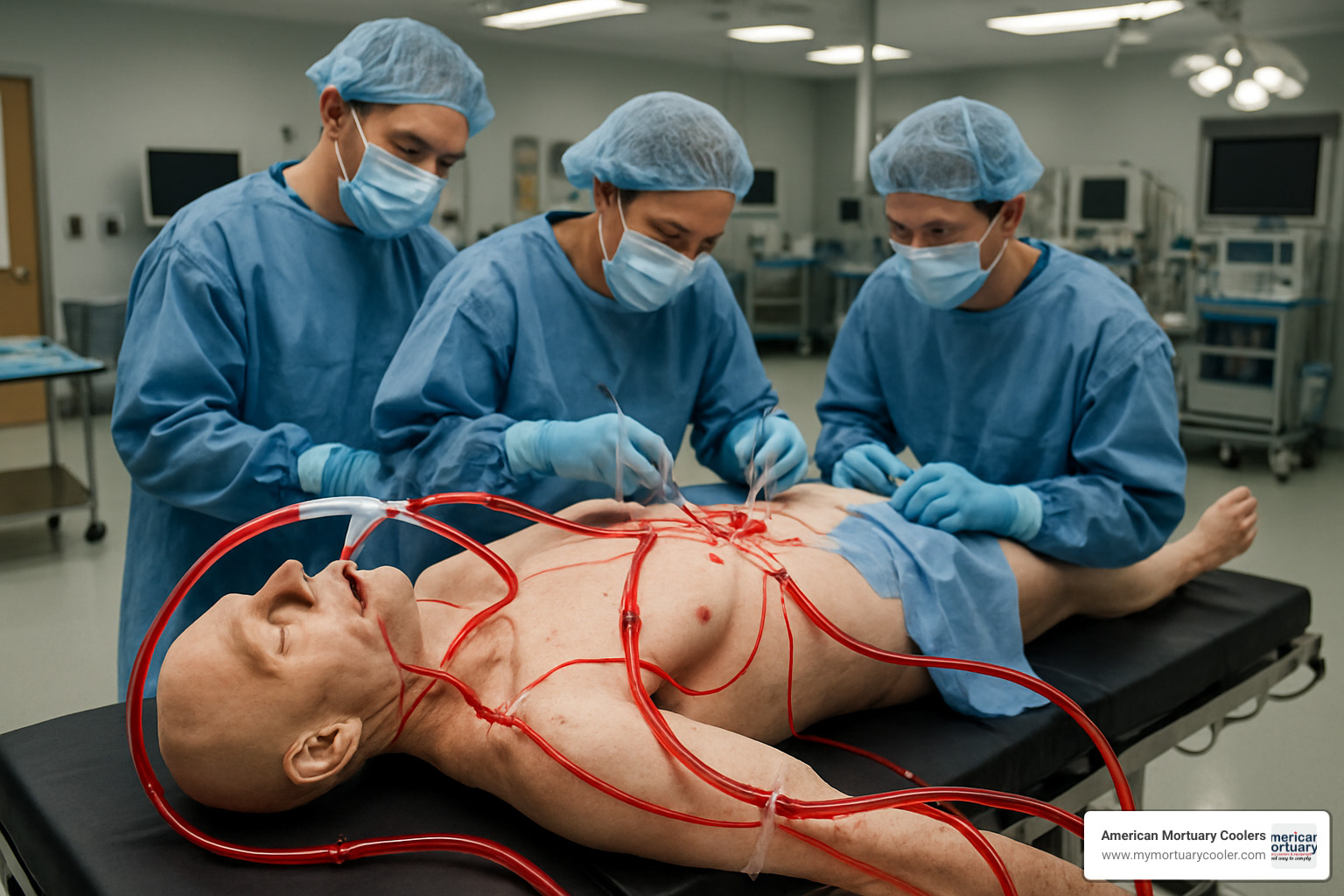
Cadaver-lab technology is evolving rapidly. Perfused cadavers with restored blood circulation provide realistic bleeding during surgical procedures, while ventilated cadaver models add breathing simulation for respiratory training.
Mobile cadaver labs solve access problems by bringing training to healthcare facilities. Companies like Acumed have developed portable units that set up in 15 minutes, democratizing medical education for rural hospitals and smaller facilities.
Part-synthetic cadaver technology combines real animal organs with synthetic human frameworks, reaching over 1.3 million students worldwide while addressing ethical concerns.
Orthopedic training particularly benefits from real human bone density and tissue response for joint replacement surgery practice. Facial anatomy applications serve the booming aesthetic medicine market, helping practitioners understand tissue layers and blood vessel patterns for safe dermal filler injections.
More info about cadaver lab locations can help find the right facility for specific training needs.
Future-Proofing the Cadaver-Lab
Green embalming techniques replace formaldehyde-heavy methods with biodegradable preservatives, addressing environmental concerns and health risks. Digital tracking systems with RFID tags manage specimens while maintaining donor anonymity.
Remote collaboration technology allows medical experts worldwide to participate in dissections through high-definition cameras and two-way audio. Hybrid preservation methods are customized for specific educational goals, while quality assurance programs ensure consistent educational experiences across facilities.
Frequently Asked Questions About Cadaver Labs
What makes a cadaver-lab irreplaceable in medical education?
The cadaver-lab provides experiences no computer or plastic model can deliver. Real human tissue builds muscle memory and spatial understanding essential for medical careers. Every cadaver shows unique anatomical variations that prepare students for real-world patient differences.
The emotional journey of working with human donors creates respect and empathy that transforms students into compassionate healthcare providers. 87% of students report better learning retention through cadaver labs, and 8 out of 10 healthcare professionals feel more confident after hands-on cadaveric training.
How are cadavers preserved, and does the method affect training quality?
Traditional formaldehyde-based preservation creates rigid, gray-colored specimens with distinctive chemical odors but provides months of study time. Thiel embalming maintains natural flexibility and coloration for more lifelike training experiences, though at higher cost.
Perfused and ventilated cadavers restore circulation and breathing for ultimate realism at around €2,000 per training day. The key is matching preservation method to learning goals - basic anatomy students work well with traditional preservation, while surgeons need advanced methods for realistic tissue response.
Can virtual reality eventually replace the traditional cadaver-lab?
Virtual reality offers impressive capabilities with unlimited repetition and clean, odor-free learning. However, the tactile feedback of feeling a human heart's weight or the pressure needed to cut muscle tissue creates irreplaceable understanding.
The future involves strategic use of both technologies - students start with virtual anatomy for foundational knowledge, progress through simulations for basic skills, then advance to cadaver-lab experience. Certain specialties like orthopedic surgery and facial anatomy will always need authentic tissue response that only cadavers provide.
Conclusion
The cadaver-lab stands as medicine's most enduring classroom, where ancient wisdom meets cutting-edge innovation. For over two millennia, human dissection has remained the gold standard for understanding the human body, with approximately 20,000 Americans annually making the extraordinary decision to become "silent teachers."
Modern facilities feature perfused cadavers with simulated blood flow, mobile training units, and advanced preservation techniques that expand access while maintaining irreplaceable hands-on experience. The numbers are compelling: 87% of medical students report better learning retention, and 8 out of 10 healthcare professionals feel more confident after cadaveric training.
Technology complements rather than replaces human anatomical study. Virtual reality and digital platforms serve important roles, but understanding tissue texture, anatomical variations, and the emotional reality of patient care requires authentic cadaver-lab experience.
The ethical foundation of voluntary donation ensures programs operate with appropriate dignity and respect. Memorial services, donor recognition ceremonies, and strict respectful handling protocols create environments where learning and reverence coexist.
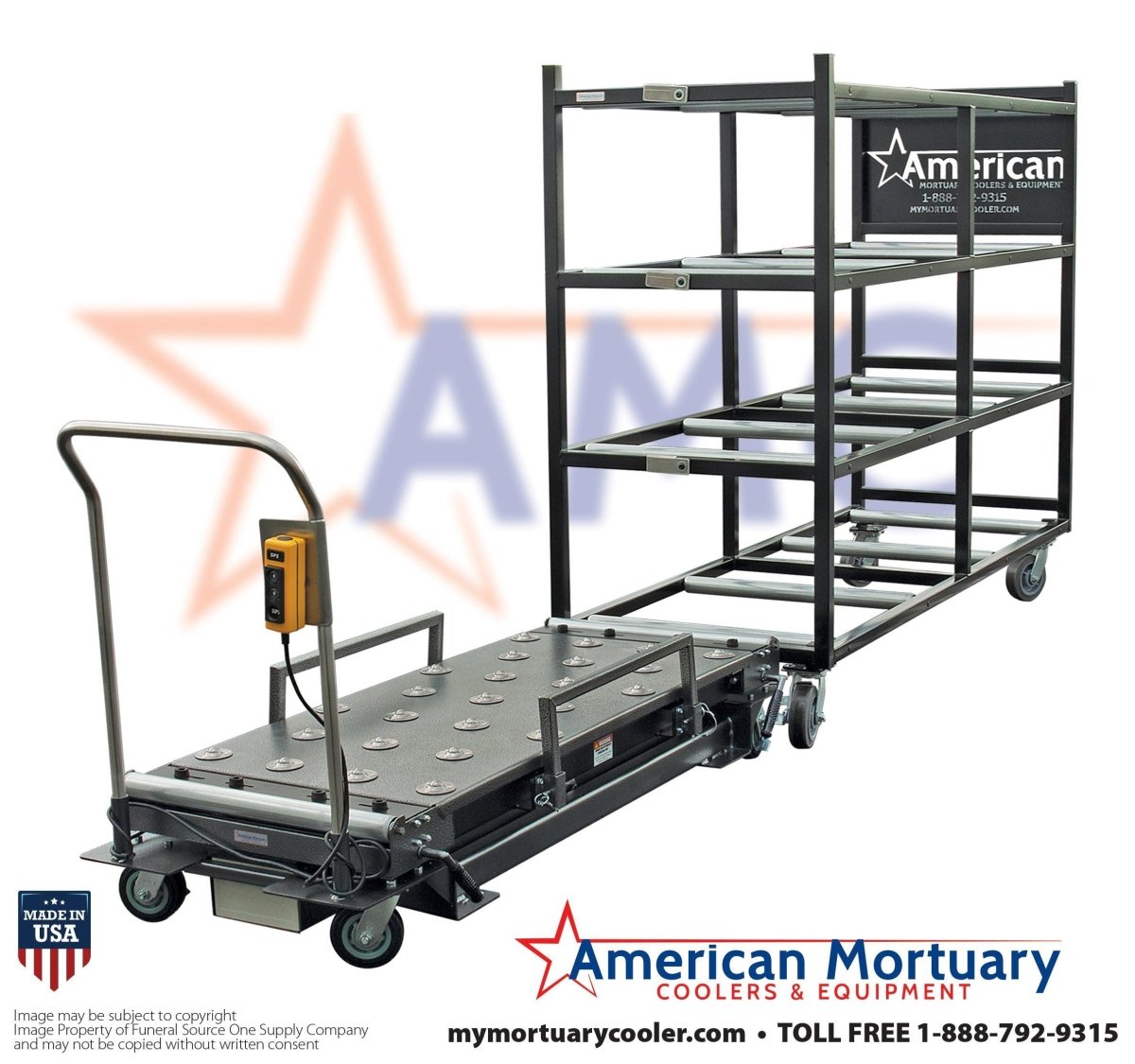
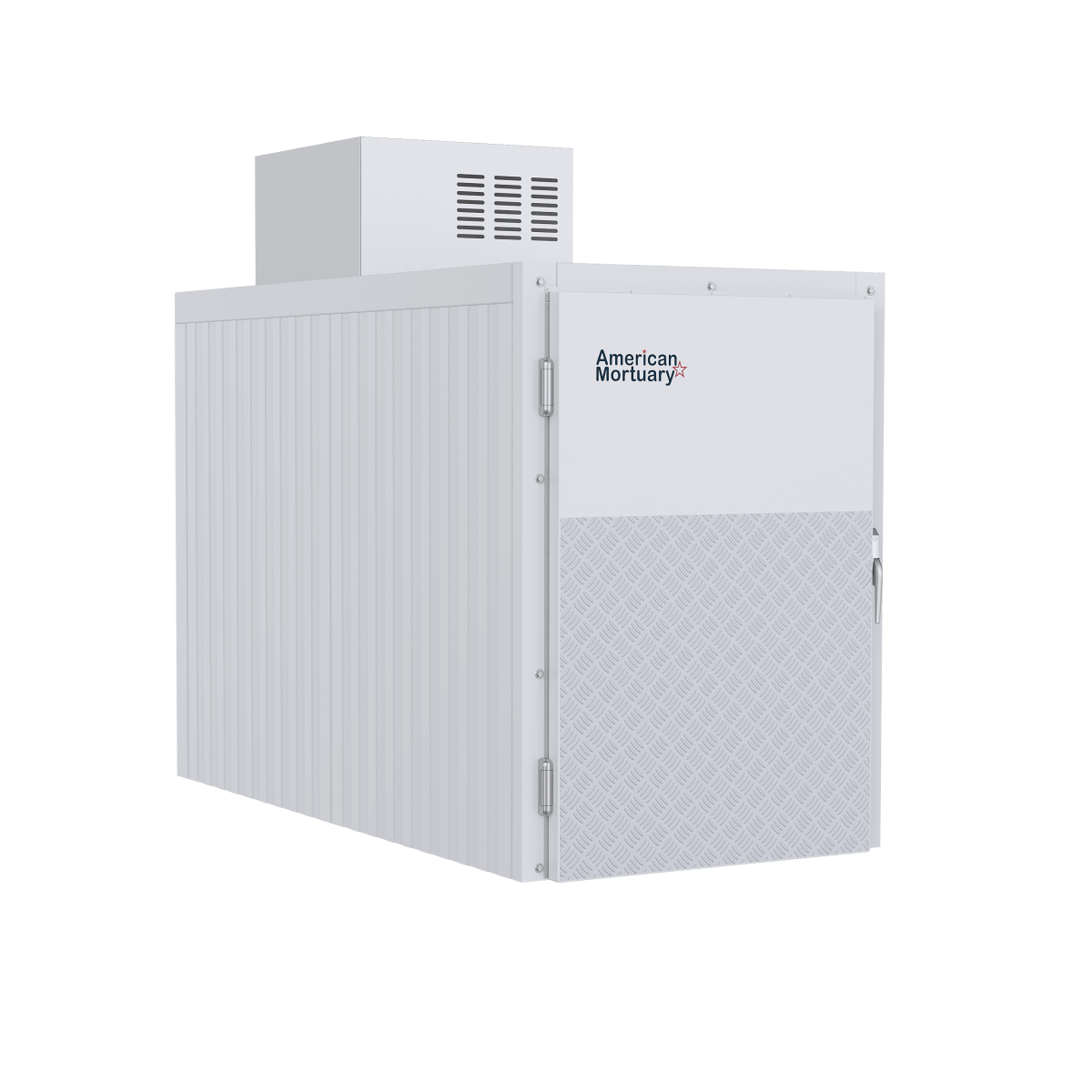
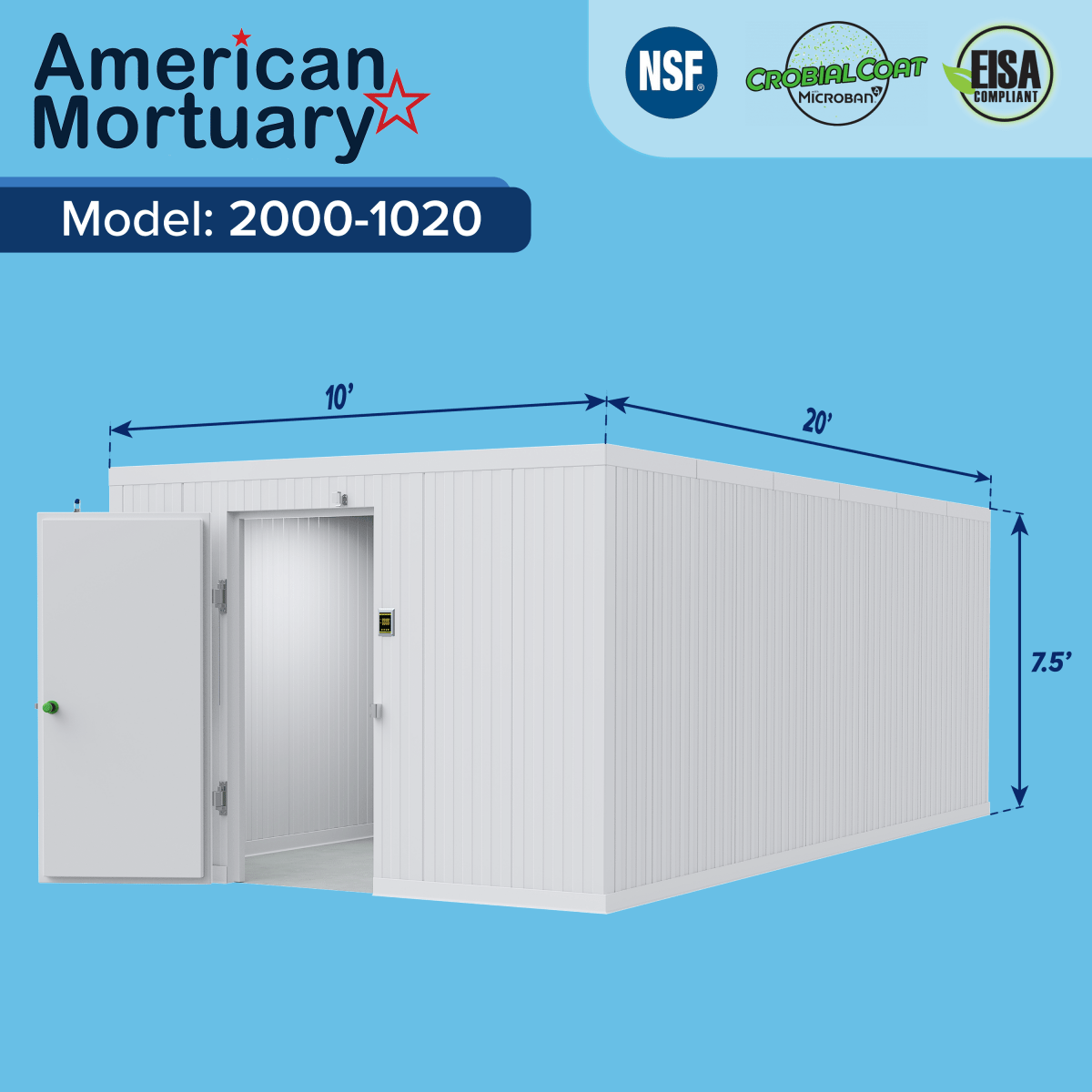
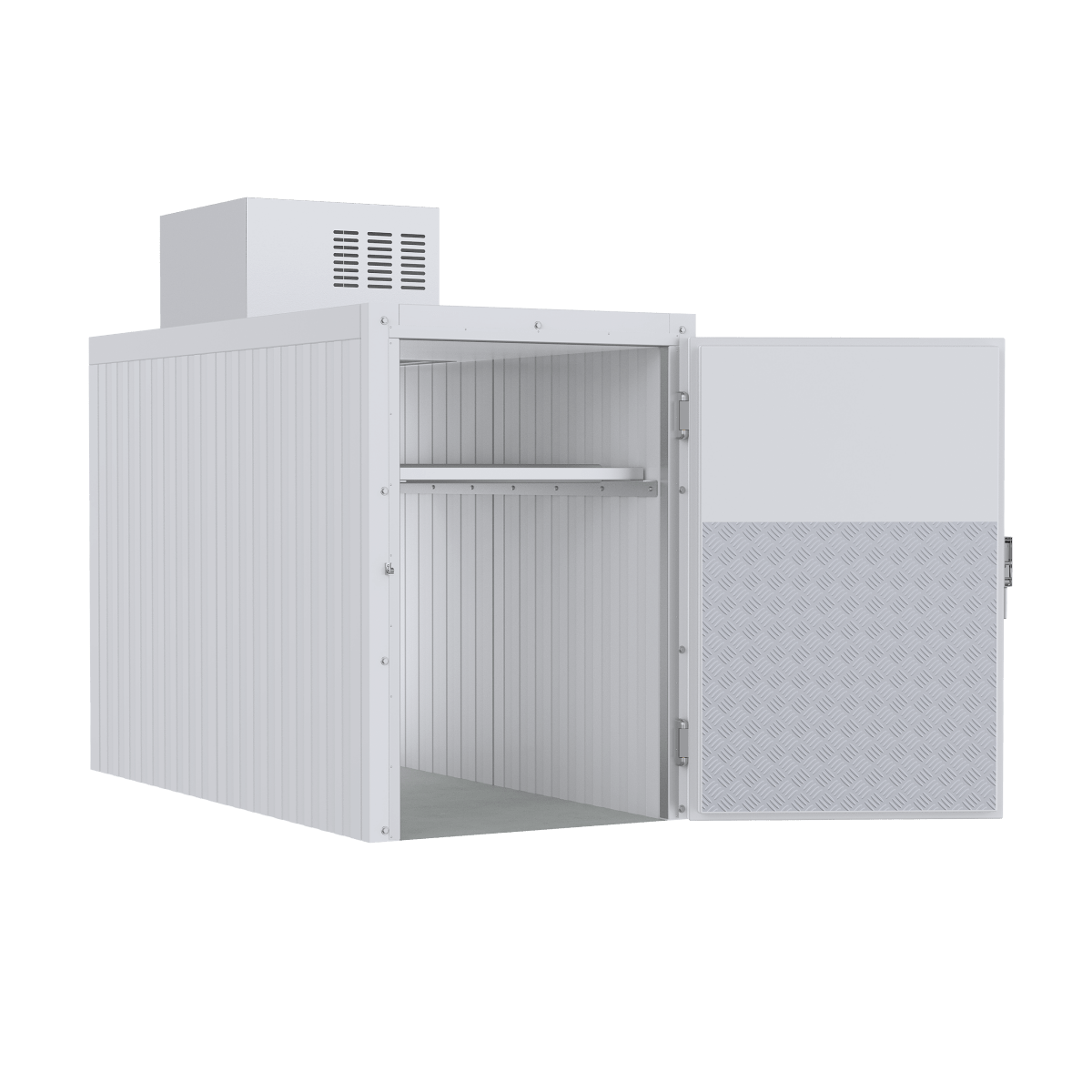
At American Mortuary Coolers, we support medical institutions across the country with infrastructure that makes quality cadaver lab education possible. Our custom storage solutions, designed and built in Tennessee, help ensure donated bodies receive proper care and respect while serving their educational mission.
From our Tennessee facility, we deliver specialized equipment to medical schools, hospitals, and training centers across all 48 contiguous states. We understand that proper storage maintains both functionality and the dignity of those who chose to continue teaching after death.
Cadaver-labs will continue serving as sacred spaces where science and humanity intersect, where students learn about both bodies and the profound responsibility of caring for human life. Whether planning new facilities, upgrading existing equipment, or ensuring current setups meet the highest standards, we're here to help with decades of experience supporting medical education infrastructure.
More info about cadaver storage racks provides detailed guidance on optimizing storage systems for maximum efficiency and respect.
Contact American Mortuary Coolers today to discuss how our custom solutions can support your cadaver-lab needs and ensure medical education continues honoring both the science of healing and the generous spirits who make it possible.