Understanding How Water Cremation Works: The Eco-Friendly Alternative
How water cremation works is a question many funeral directors are asking as this eco-friendly alternative gains popularity in 2025. Also known as aquamation or alkaline hydrolysis, water cremation offers a gentle, sustainable approach to final disposition.
Quick Facts About Water Cremation:
| Aspect | Details |
|---|---|
| Process | Uses water, alkaline chemicals, heat, and sometimes pressure to accelerate natural decomposition |
| Duration | 4-6 hours at higher temperatures or 14-16 hours at lower settings |
| Temperature | Typically 150-350°F (much lower than flame cremation's 1500°F+) |
| Energy Usage | Uses about 90% less energy than traditional flame cremation |
| Emissions | Produces zero emissions and uses no fossil fuels |
| End Result | White bone fragments processed into powder (about 32% more than flame cremation) |
Water cremation mimics the natural decomposition process but accelerates it from years to just hours. The body is placed in a stainless steel vessel with a solution of 95% water and 5% potassium hydroxide.
This gentle process has caught public attention partly due to influential figures like Archbishop Desmond Tutu, who chose water cremation for his own final arrangements in 2022. As climate concerns grow in 2025, more funeral homes are considering this option for families seeking environmentally conscious choices.
Unlike traditional flame-based cremation, water cremation doesn't release mercury from dental fillings or other harmful emissions into the air. The sterile effluent is 96% water and can be safely returned to the ecosystem, often repurposed as fertilizer.
For funeral directors looking to expand their service offerings, understanding this process is increasingly important as public awareness and demand continue to rise.
Quick Insight 1: What Is Water Cremation and How Does It Differ From Traditional Cremation?
Water cremation, technically known as alkaline hydrolysis, offers a gentle alternative to traditional flame-based methods. At its essence, this process harnesses water, alkaline chemicals, heat, and sometimes gentle agitation to speed up what nature would do on its own. The Cremation Association of North America officially recognizes it as "a water‐based dissolution process that uses alkaline chemicals, heat, and sometimes agitation and/or pressure, to accelerate natural decomposition."
Many families appreciate that water cremation provides a more peaceful journey for their loved ones compared to traditional flame cremation. There's something comforting about the gentler approach of water versus fire.
How water cremation works differently from flame cremation becomes clear when we look at the details. Traditional cremation uses intense fire and extreme temperatures that can feel harsh and industrial. Water cremation, by contrast, feels more natural and dignified to many families seeking closure.
The differences between these two approaches are significant:
Temperature needs for water cremation are much gentler—only 150-350°F compared to the scorching 1500°F+ required for flame cremation. Energy use is dramatically reduced, with water cremation using just one-quarter of the electricity needed for traditional methods (about 90 kWh). Environmental impact is another major difference—traditional cremation releases carbon dioxide and mercury from dental fillings into our air, while water cremation produces zero emissions. Time requirements vary too, with flame cremation taking about two hours while water cremation requires 4-6 hours at higher temperatures or 14-16 hours at gentler settings. The resulting remains from water cremation are about 32% more plentiful and have a finer, whiter texture than flame cremation ashes. And finally, the fundamental process differs—flame cremation burns the body while water cremation dissolves soft tissues, leaving only bone fragments behind.

Understanding How Water Cremation Works at a Basic Level
How water cremation works mirrors what happens naturally when a body returns to the earth—just much faster. When we bury someone, their body gradually breaks down through natural alkaline hydrolysis as water, soil pH, and bacteria work together. Water cremation simply accelerates this respectful process that's been happening in nature since the beginning of time.
The technology looks deceptively simple—a specially designed stainless steel vessel holding about 100 gallons of liquid. But this equipment requires sophisticated engineering to maintain precise pressure and temperature throughout the process. Modern units feature careful controls that ensure everything proceeds with dignity and efficiency.
Julian Atkinson, who knows the industry well, explains the human side of introducing this technology: "With anything new, you have to win over people and build understanding. To bring water cremation forward, we had to gain planning permission to set up the facility and consent from the local water board."
The gentle process combines four elements working in harmony: water as the primary medium, an alkaline solution (typically potassium hydroxide), gentle heat maintained below boiling, and sometimes soft agitation or pressure. Together, these elements respectfully break down the body's proteins, fats, and other soft tissues. What remains are only the bone minerals, which are then processed into a fine powder similar to what families receive after traditional cremation.
For funeral directors considering this option for families, the process represents both environmental responsibility and a gentler approach that many find comforting during difficult times.
Quick Insight 2: How Water Cremation Works – The Detailed Process Explained
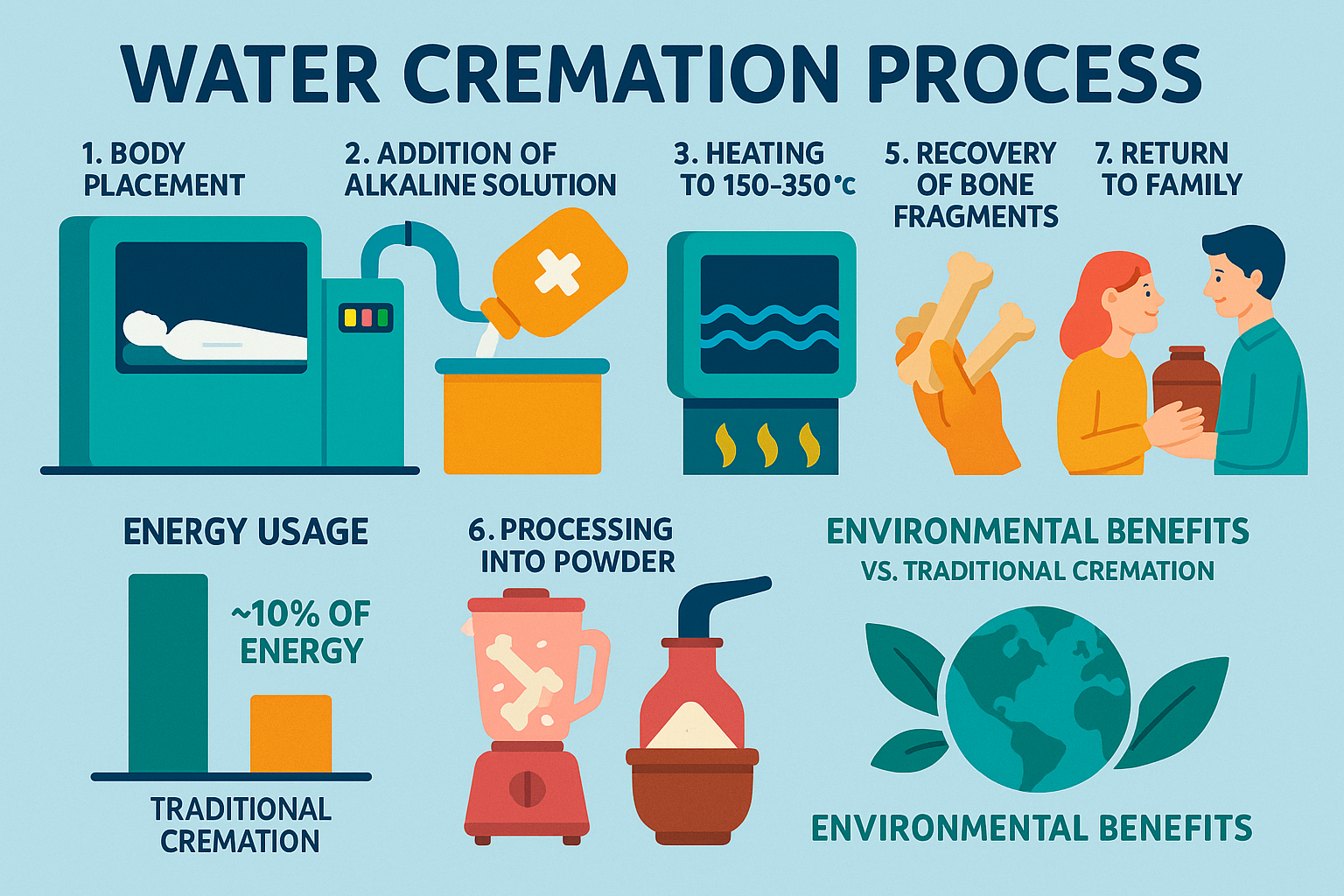
Now let's examine exactly how water cremation works through a detailed step-by-step explanation of the process:
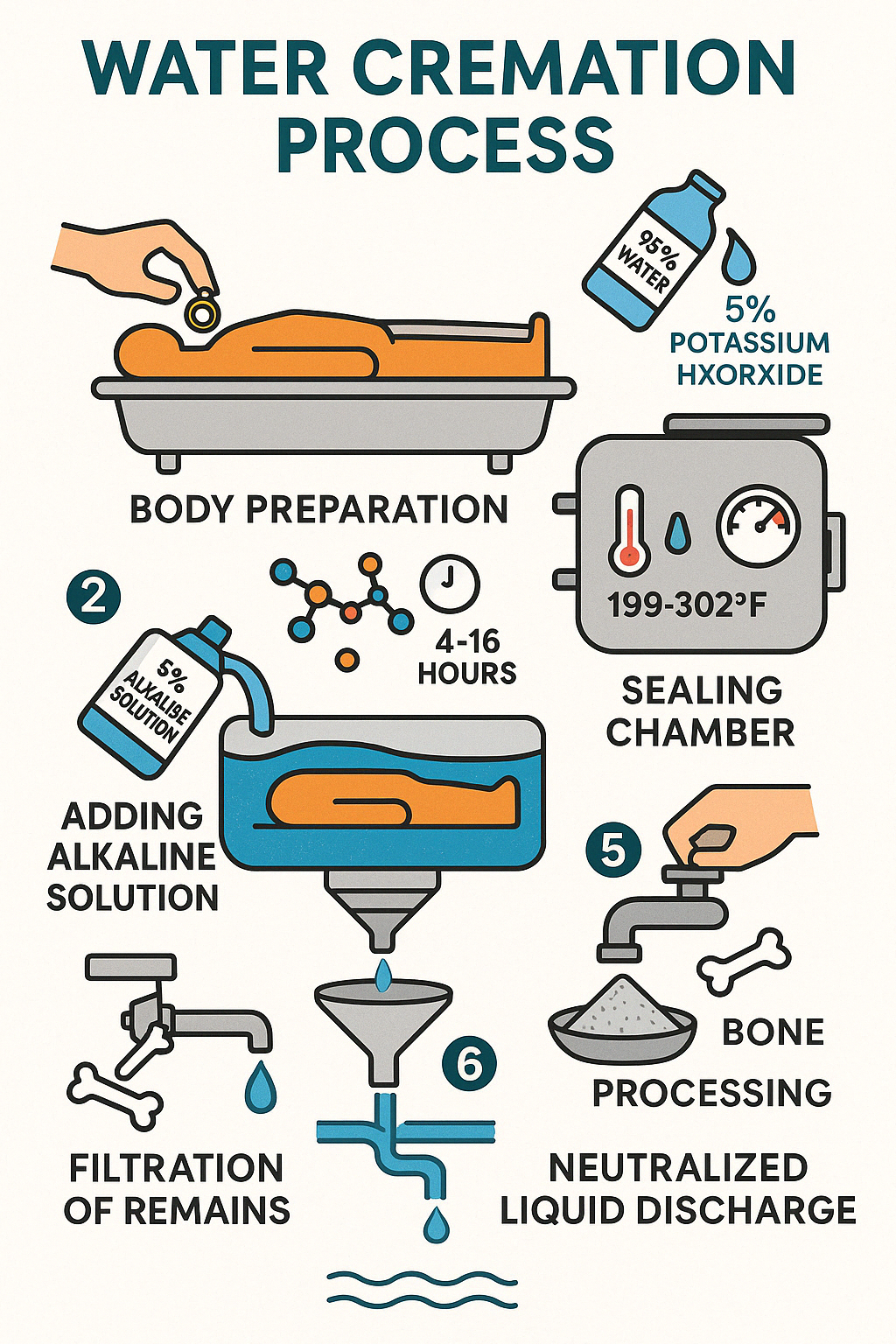
Step 1: Preparation
The deceased is respectfully placed in a stainless steel vessel. Unlike flame cremation, there's no need for a combustible container or coffin. Personal items like jewelry are carefully removed beforehand—a thoughtful touch since these items can be returned to the family intact, something impossible with traditional cremation where they would be destroyed by the intense heat.
Step 2: Introduction of Solution
Once the body is positioned, about 80 gallons of solution is added to the vessel. This solution is primarily water (approximately 95%) mixed with potassium hydroxide (about 5%). The exact alkalinity is carefully calibrated based on several factors, including the size of the body, ensuring a gentle and effective process.
Step 3: Sealing and Activation
With everything in place, the vessel is securely sealed, and the process begins. The solution is warmed to a temperature between 199°F and 302°F (93-150°C)—significantly cooler than flame cremation's 1500°F+ temperatures. Some advanced systems apply a small amount of pressure to keep the water in its liquid state at these temperatures, enhancing the efficiency of the process.
Step 4: The Breakdown Process
Over the next several hours—typically 4-16 hours depending on the equipment and settings—nature takes its course, only faster. The warm alkaline solution, sometimes with gentle agitation, breaks down the body's soft tissues. This isn't a harsh chemical destruction but rather an accelerated version of natural decomposition. Proteins, fats, and other organic materials gracefully transform into their basic components: amino acids, peptides, sugars, and soaps.
Step 5: Completion and Bone Processing
When the cycle completes, the vessel contains only bone fragments and a sterile liquid. The bones, now softened but still intact, are carefully removed and dried. These fragments then undergo processing in a cremulator (similar to traditional cremation) to create a fine, white powder. Families often comment on how the remains are noticeably whiter and finer than those from flame cremation—many find this aesthetically pleasing when choosing an urn or scattering option.
Step 6: Effluent Management
The remaining liquid is sterile and contains no DNA or tissue—it's essentially a solution of basic organic compounds. This liquid is treated to neutralize its pH before being discharged. Many facilities have found that this nutrient-rich solution makes excellent fertilizer, bringing a sense of renewal to the process.
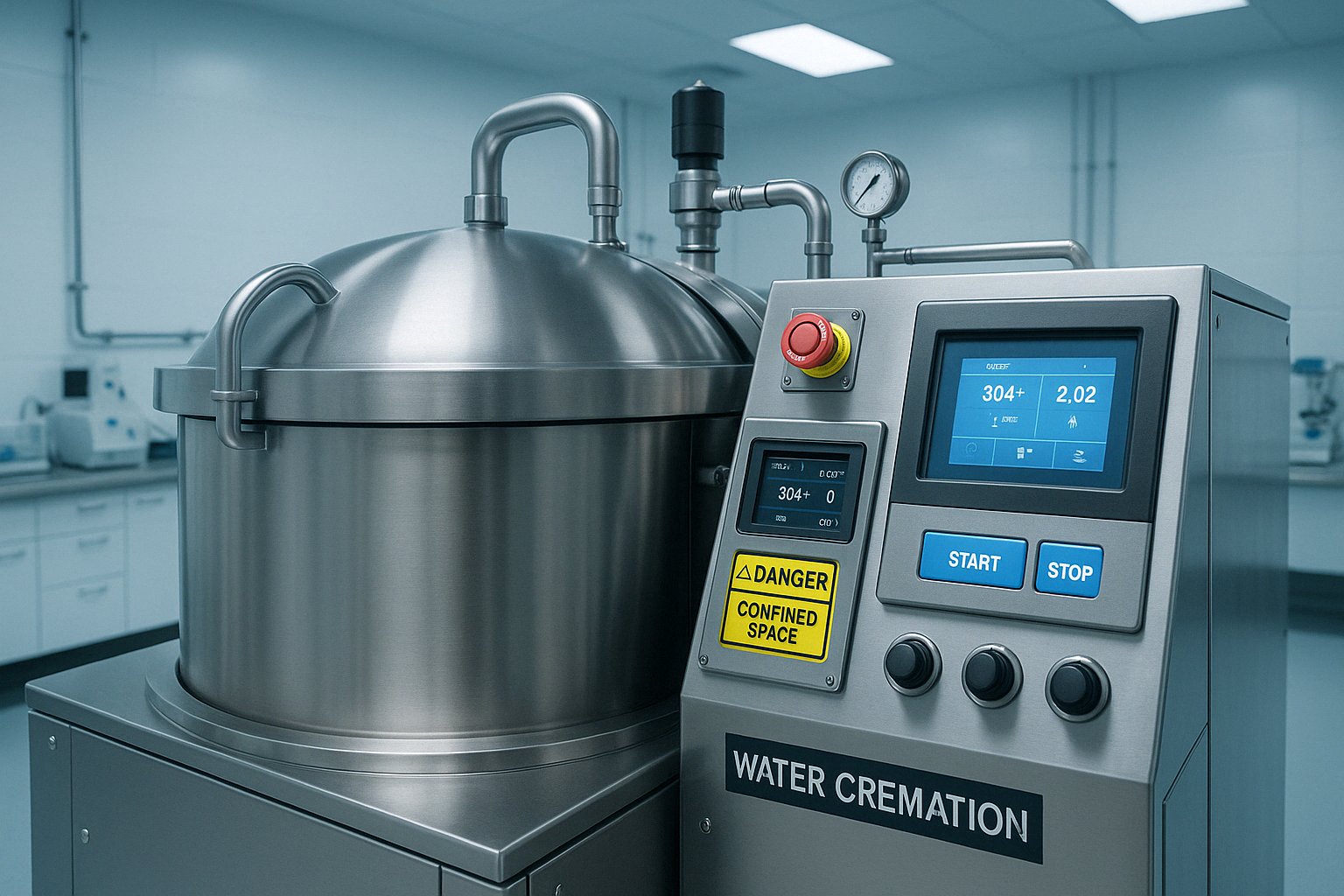

The Science Behind How Water Cremation Works
The chemistry behind how water cremation works is both fascinating and neat. At its heart is alkaline hydrolysis—a natural process that breaks the chemical bonds in organic materials. Here's what happens beneath the surface:
The high-pH alkaline solution (around 14 on the pH scale) gently breaks the bonds between hydrogen and nitrogen in the body's proteins through hydrolysis. This is similar to what happens in nature, just much faster.
Meanwhile, body fats undergo saponification—yes, the same process used to make soap! The alkaline solution transforms fats into fatty acid salts (essentially soap) and glycerol. This is why the resulting liquid feels slippery, much like soapy water.
Proteins don't just disappear—they're denatured and broken down into their building blocks: amino acids. As cellular structures dissolve, what was once complex tissue returns to simple molecular components.
The beauty of this process is what doesn't happen: no combustion means no airborne emissions of mercury (from dental fillings), carbon dioxide, or other pollutants. The energy required is substantially less than flame cremation, and the entire process can run on electricity rather than fossil fuels.
As one funeral director who recently adopted the technology told us: "Families are increasingly concerned about their environmental footprint, even after death. When I explain how water cremation works and its gentler impact on our planet, many find comfort in choosing this option for their loved ones."
For those interested in diving deeper into the science, the Alkaline Hydrolysis Explained: The Science Behind Water Cremation article on our site offers more technical details. You can also explore the Water cremation - Wikipedia page for additional information.
Quick Insight 3: Environmental and Legal Considerations of Water Cremation
When families learn how water cremation works, they're often most impressed by its environmental benefits. This gentle process is quickly becoming the choice for those concerned about their final environmental footprint in 2025.
Environmental Benefits
Water cremation stands out as a remarkably eco-friendly option in the funeral industry. Unlike traditional flame cremation that consumes massive amounts of energy to reach temperatures over 1500°F, water cremation uses just a fraction of that energy—about 90 kWh of electricity, which is less than one-fifth of what flame cremation requires.
Perhaps most impressive is the complete absence of emissions. Traditional cremation releases carbon dioxide, particulates, and mercury from dental fillings directly into our atmosphere. With water cremation, there's simply nothing going up the chimney. When powered by renewable electricity sources, it can be essentially carbon-neutral.

While the process does use water—about 80-100 gallons, similar to what a family of four might use in a day—this water doesn't go to waste. In many areas, the nutrient-rich effluent can be recycled as fertilizer, completing a natural cycle of return to the earth.
Another practical advantage is that medical implants like pacemakers, artificial joints, and dental work remain intact after water cremation. These can be properly recovered and recycled rather than being incinerated, which further reduces environmental impact.
| Aspect | Water Cremation | Flame Cremation | Traditional Burial |
|---|---|---|---|
| Energy Use | 90 kWh (1/4 of flame cremation) | 360 kWh | Varies (embalming, casket production) |
| Carbon Emissions | Minimal (electricity only) | 150-300 kg CO2 | 50-100 kg CO2 (less if green burial) |
| Water Usage | ~80-100 gallons | Minimal | Minimal |
| Land Use | None | None | Significant |
| Chemical Use | 5% potassium hydroxide | None | Embalming chemicals |
| Mercury Emissions | None (captured) | 2-4 grams per cremation | None |
| Resource Recovery | Metals can be recovered | Metals destroyed | Resources buried |
The growing interest in these environmental benefits isn't just anecdotal. The National Funeral Directors Association reports that as of 2025, interest in "green" funeral options has continued to climb, with nearly 65% of consumers now expressing interest in environmentally friendly alternatives—a significant increase from previous years.
Legal Status and Regulations
Despite its environmental advantages, the availability of water cremation varies widely depending on where you live. The legal landscape in 2025 shows continued progress:
In the United States, more than 35 states have now legalized water cremation for human remains, with around 50 facilities operating in approved areas. This represents significant growth since the early 2020s, though some states are still working through the regulatory process.
Canada has made substantial progress, with most provinces now approving the process. The United Kingdom has fully implemented water cremation services, while Australia continues to expand its offerings since first introducing the service in 2010.
"With over 10,000 dispositions in the United States by 2025, water cremation's global growth is well underway."
The regulatory challenges typically involve updating existing cremation definitions to include water-based processes, addressing wastewater regulations, and establishing proper facility requirements. The funeral industry continues to play a key role in shaping these regulations, with increasing support for this eco-friendly alternative.
Sandy Sullivan, a pioneer in water cremation technology, puts it well: "Resomation exists to ensure the choice of water cremation is available globally. This will be achieved through increasing public awareness, education, industry acceptance and legislative change."
For families interested in this option, it's worth checking the current legal status in your state. You can learn more about the laws in your area through resources like Water Cremation and Aquamation Laws in Your State.
Influential Figures and Growing Public Awareness
When Archbishop Desmond Tutu, the Nobel Peace Prize laureate and anti-apartheid leader, chose water cremation for his own funeral in 2022, people around the world took notice.
Tutu had long been an environmental advocate, and his final choice served as a powerful statement about ecological responsibility. His decision brought international attention to how water cremation works and sparked conversations about sustainable funeral practices worldwide.
You can learn more about Archbishop Tutu's choice in What is aquamation? The process behind Desmond Tutu's 'green cremation'.
The impact of Tutu's choice continues to resonate in 2025. Current data shows that when given the option between water and flame cremation, approximately 85% of families now choose water cremation, citing both environmental concerns and the gentler nature of the process.
Howard Pickard, an industry managing director, notes: "Having been associated with Resomation from its inception, we have seen how water cremation presents the public with a credible environmentally sustainable funeral choice, something that is becoming more and more important in the fight against climate change."
As awareness grows, so does the adoption of this technology. Dr. Emily McClatchey humorously observes: "Water cremation known by any other name (Alkaline Hydrolysis, Aquamation, Flameless Cremation, Resomation, Biocremation) is still water cremation." The variety of terms reflects the industry's ongoing efforts to find language that resonates with families while accurately describing this gentle process.
For funeral directors considering adding this option to their services, the environmental benefits and growing consumer interest make a compelling case for exploring how water cremation works and how it might fit into their offerings.
Frequently Asked Questions About How Water Cremation Works
Is Water Cremation Legal in My State?
Navigating the legal landscape of water cremation can feel a bit like watching legislation in motion. The good news is that how water cremation works is becoming better understood by lawmakers, with over 35 states now permitting this gentle alternative to flame cremation as of 2025.
Currently, water cremation is legal in Alabama, California, Colorado, Connecticut, Florida, Georgia, Hawaii, Idaho, Illinois, Indiana, Iowa, Kansas, Kentucky, Maine, Maryland, Massachusetts, Michigan, Minnesota, Missouri, Montana, Nebraska, Nevada, New Hampshire, New Jersey, New Mexico, New York, North Carolina, Ohio, Oregon, Pennsylvania, Rhode Island, Tennessee, Utah, Vermont, Washington, and Wyoming—with more states considering legislation each year.
But here's the thing to keep in mind: even where it's legal, you might not find it readily available. Funeral homes need specific permits and specialized equipment to offer water cremation. At American Mortuary Coolers, we're passionate about helping funeral directors understand their state's requirements and steer the regulatory waters (pun intended).
If you're in a state where water cremation isn't yet permitted, don't lose hope. Many industry professionals are actively advocating for expanded availability. Joining these efforts through professional associations can help bring this eco-friendly option to more families across the country.
What Happens to the Water After the Process?
One of the most common questions we hear about how water cremation works concerns the liquid that remains afterward. Rest assured, this isn't something to worry about—the resulting effluent is completely sterile, containing no DNA or tissue.
This liquid—about 96% water mixed with salts, amino acids, peptides, sugars, and nutrients—is essentially a solution of the body's basic building blocks. Before disposal, technicians adjust the pH to at least 11 to ensure safety.
From there, the liquid typically follows one of three paths:
Most commonly, it's discharged to municipal wastewater treatment facilities, where it's processed alongside other wastewater. In some forward-thinking regions, this nutrient-rich solution finds new purpose as fertilizer for non-food crops or tree farms—turning what would be waste into a resource. Some facilities have even created closed-loop systems, using the treated effluent for on-site landscaping.
What makes this particularly remarkable is the contrast with flame cremation. Instead of releasing emissions into the air, water cremation returns nutrients to the earth—completing a natural cycle in a gentler way.
How Much Does Water Cremation Cost Compared to Traditional Methods?
When families ask about the cost of water cremation in 2025, they're often relieved to hear it's in the same ballpark as traditional cremation. While prices vary by region and provider, water cremation typically ranges from $1,800 to $3,500, with an average of around $2,980 for a simple package.
For comparison, flame cremation usually costs between $1,200 and $2,800, while traditional burial averages a much higher $8,000 to $15,000 when you include the casket, vault, and cemetery plot.
For funeral homes considering adding this service, there are some business factors to consider. The initial investment in water cremation equipment is typically higher than traditional cremation equipment. The process also takes longer—4-16 hours versus flame cremation's 2 hours—which affects how many services a facility can perform daily.
On the flip side, water cremation uses significantly less energy, though it does require water and alkaline chemicals. Many funeral directors find that offering this eco-friendly alternative attracts environmentally conscious families who might otherwise choose direct cremation or green burial options.
At American Mortuary Coolers, we work closely with funeral directors to understand all aspects of adding water cremation to their services—from equipment needs to facility requirements. We believe in helping our partners make informed decisions that serve both their business needs and the families who come to them during difficult times.
Conclusion
Water cremation represents a significant advancement in funeral technology, offering a gentler, more environmentally friendly alternative to traditional methods. As we've explored through these three quick insights, how water cremation works involves a natural process that accelerates decomposition using water and alkaline chemicals rather than fire.
The journey through understanding water cremation reveals why this option is gaining traction among environmentally conscious families in 2025. When we look at the energy savings—a remarkable 90% reduction compared to flame cremation—it's easy to see why funeral directors are fielding more questions about this service. The gentle nature of the process, operating at temperatures similar to a hot cup of coffee rather than the intense heat of traditional cremation, appeals to many families seeking a more natural approach.
Families often appreciate receiving the slightly greater amount of remains that water cremation provides. These remains are notably different too—whiter, finer, and more abundant by about a third. For many, this creates a more meaningful keepsake to honor their loved one.
The environmental story of water cremation is perhaps its most compelling chapter. Without the burning process, there's no release of mercury from dental fillings, no carbon emissions contributing to climate change, and potentially even a beneficial afterlife for the nutrients that return to the earth. It's a full-circle approach that resonates deeply with those concerned about their final footprint.
Legal acceptance continues to grow, with more than 35 U.S. states now permitting water cremation as of 2025. This momentum, bolstered by high-profile advocates like Archbishop Desmond Tutu, signals a shifting landscape in funeral practices where sustainability matters more than ever before.
At American Mortuary Coolers, we're right beside funeral directors as they steer these evolving technologies and changing consumer preferences. From our home base in Tennessee with locations throughout the United States, we provide not just equipment but also the expertise needed to successfully introduce these eco-friendly options to your community.
Climate consciousness is no longer just a consideration for life—it's increasingly important in death as well. Water cremation stands as an innovation that honors both our planet and our loved ones with equal dignity. The greening of funeral services isn't just a trend; it's a change in how we think about our final arrangements.
For more information on water cremation equipment and how American Mortuary Coolers can support your facility's needs, contact our team serving the entire contiguous United States from our regional locations in Johnson City TN, Atlanta GA, Chicago IL, Columbia SC, Dallas TX, Los Angeles, New York NY, and Pittsburgh PA.