Why C1D1 Certification Is Critical for Safe Operations
C1d1 certification is a mandatory safety requirement for facilities handling flammable gases, vapors, or liquids under normal operating conditions. This certification ensures that electrical equipment and facility designs meet strict National Fire Protection Association (NFPA) standards to prevent explosions and protect workers.
Quick Answer for C1D1 Certification:
- What it is: Class I, Division 1 hazardous location certification under NFPA 70
- When required: Areas with flammable substances present during normal operations
- Key equipment: Explosion-proof lighting, sealed conduit, intrinsically safe devices
- Certification bodies: UL, CSA, Explosion Research Ltd., MET Labs
- Renewal: Annual inspections, recertification every 3 years
- Non-compliance cost: OSHA fines over $100,000, average accident loss $250,000
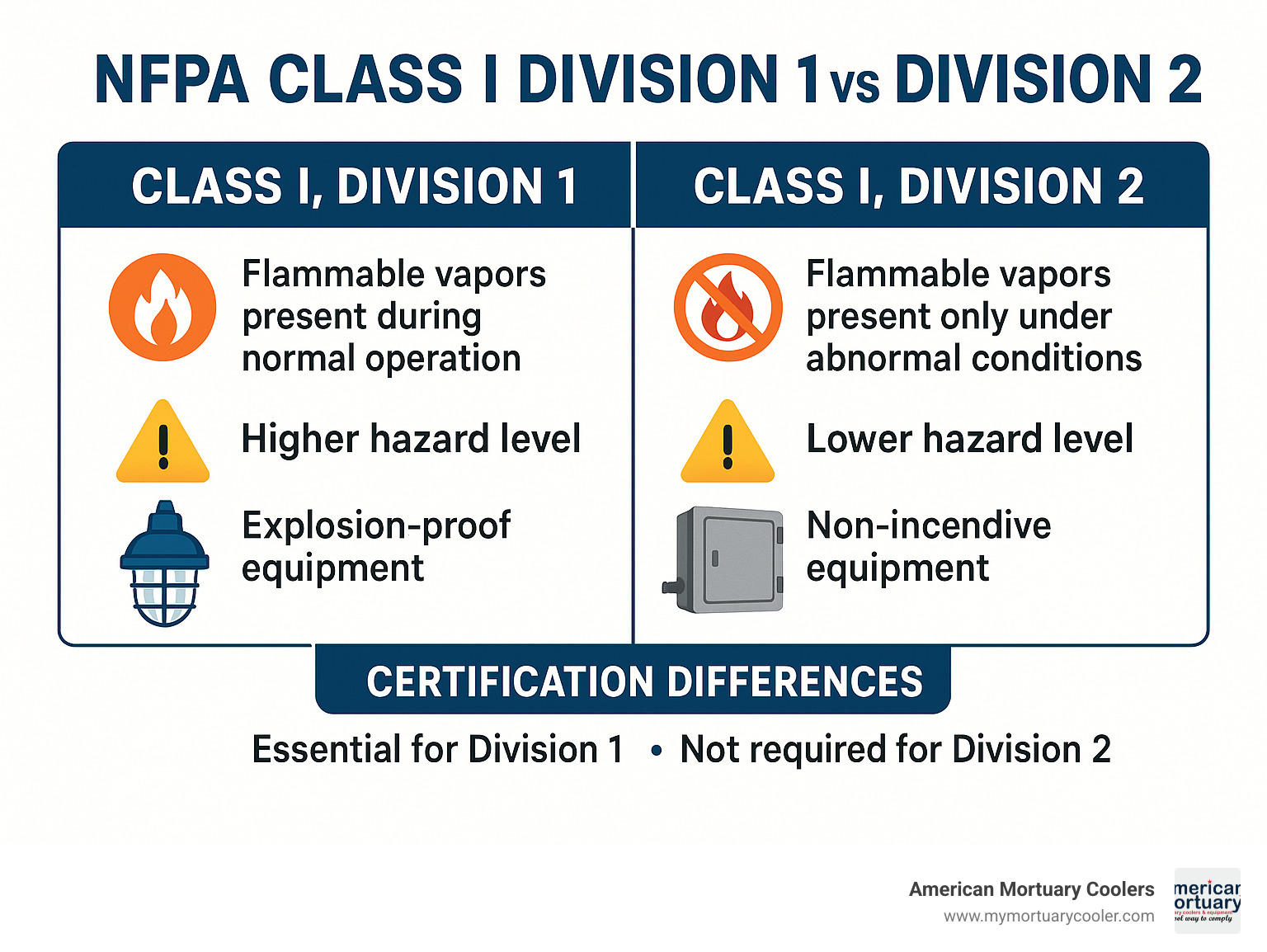
C1D1 areas are the most dangerous - where flammable gases or vapors can ignite under normal conditions. Unlike C1D2 areas that only pose risks during equipment failures, C1D1 zones require the highest level of protection.
According to NFPA data, over 60% of oil and gas processing facilities in North America contain C1D1 hazardous locations. OSHA enforcement data shows fines exceeding $100,000 for safety violations, while explosion-related incidents average $250,000 in losses.
Industries from cannabis extraction labs to chemical processing plants depend on proper c1d1 certification to operate safely and legally. Even mortuary facilities using certain refrigeration systems may need these requirements.
I'm Mortuary Cooler from American Mortuary Coolers, and I've helped funeral homes steer complex safety regulations including c1d1 certification requirements for specialized equipment installations.
Simple c1d1 certification word guide:
What Is C1D1 Certification?
C1d1 certification stands for Class I, Division 1 hazardous location certification under NFPA 70, part of the National Electrical Code (NEC Article 500).
Class I means flammable gases, vapors, or liquids that could explode. Division 1 means these hazardous substances are present during normal, everyday operations. The system includes Groups A through D, classifying specific gases by ignition ease and explosion pressure.
C1D1 areas are always dangerous because flammable atmospheres exist continuously. Every electrical component must be explosion-proof or intrinsically safe.
| Feature | C1D1 Requirements | C1D2 Requirements |
|---|---|---|
| Hazard Presence | Continuous/normal operations | Abnormal conditions only |
| Equipment Type | Explosion-proof mandatory | Dust-ignition-proof acceptable |
| Conduit Requirements | Threaded rigid metal, sealed within 18" | Flexible methods permitted |
| Energy Limits | Below ignition thresholds always | Avoid arcing during normal operation |
Key Differences Between C1D1 Certification and C1D2 Classification
C1D1 areas are always dangerous with flammable gases present continuously. All equipment needs explosion-proof enclosures and threaded rigid metal conduit with sealed fittings within 18 inches.
C1D2 areas are dangerous only during failures - hazardous substances appear during equipment malfunctions or maintenance. Dust-ignition-proof enclosures and flexible wiring methods are acceptable.
Why Industrial & Lab Facilities Need C1D1 Certification
Worker safety prevents explosions from static electricity or loose connections. OSHA fines under 29 CFR 1910.307 exceed $100,000 for violations. Liability protection reduces insurance premiums and protects against claims.
NFPA data shows properly certified facilities experience 95% fewer explosion-related incidents than non-compliant operations.
Regulatory Framework & Safety Standards Governing C1D1
C1d1 certification involves multiple organizations creating and enforcing safety standards for hazardous locations.
The National Fire Protection Association (NFPA) creates NFPA 70 (National Electrical Code), specifically Article 500 defining c1d1 certification requirements.
OSHA enforces these standards through workplace safety regulations, conducting inspections and issuing fines for non-compliance.
International standards from the International Electrotechnical Commission (IEC) apply to global equipment and operations.
Core Standards You Must Meet
NFPA 70 Article 500 covers hazardous area classification, equipment selection, and installation requirements including conduit sealing and junction boxes.
OSHA regulation 1910.307 makes employers responsible for proper hazardous location classification and worker training.
IEC 60079 standards use a "zone" system instead of "division" system but maintain the same safety goals.
UL 913 addresses intrinsically safe equipment that limits electrical energy and surface temperatures below dangerous levels.
Approved Certification Bodies & Required Paperwork
Underwriters Laboratories (UL) provides the most recognized North American certification with ongoing factory inspections.
CSA Group offers certification valuable for Canadian operations and cross-border facilities.
MET Labs and Explosion Research Ltd. provide alternatives with specialized expertise and faster turnaround.
Documentation includes detailed engineering drawings, hazardous area classification studies, equipment specifications with certification markings, training records, and control drawings.

Design & Equipment Requirements for C1D1 Areas
C1d1 certification requires specific design features preventing ignition sources or safely containing explosions.
Essential Design Elements:
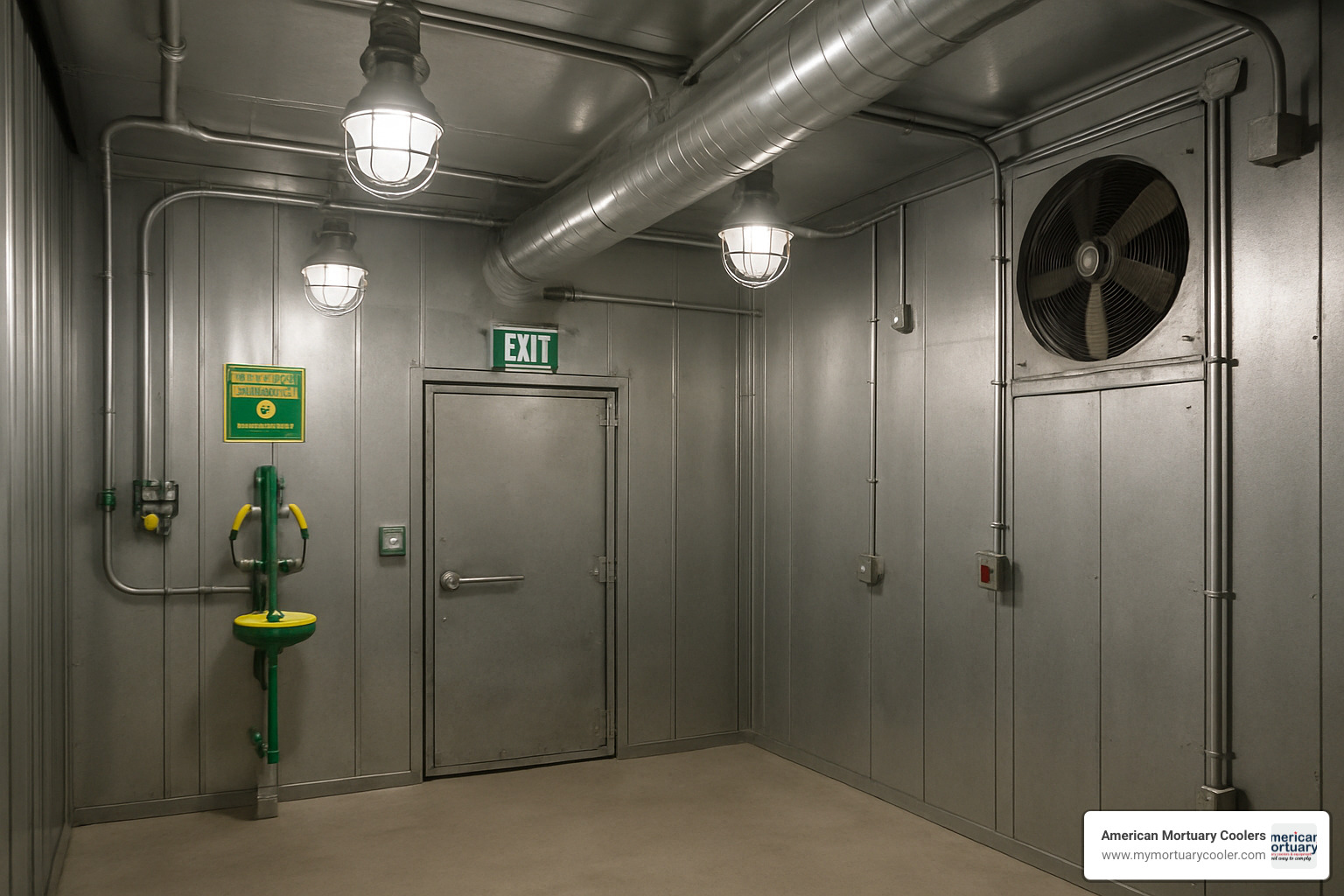
- Explosion-proof enclosures: Contain internal explosions and prevent flame propagation
- Intrinsically safe circuits: Limit energy to prevent ignition under fault conditions
- Sealed conduit systems: Prevent gas migration between areas
- Proper ventilation: Maintain safe atmosphere through adequate air changes
- Gas detection systems: Provide early warning of hazardous conditions
Ventilation Requirements: C1D1 areas need high air exchange rates with explosion-proof fans. Proper ventilation with gas detection decreases hazardous vapor incidents by over 80%, requiring explosion-proof fans, balanced intake/exhaust systems, emergency shutdown capabilities, and gas detection integration.
Construction Standards: C1D1 rooms feature interlocking steel panel construction with single or double-wall insulation between 20-gauge steel sheets. More info about walk-in cooler features provides insights into specialized enclosure design.
Equipment That Must Be C1D1 Certified
Lighting Systems: Explosion-proof fixtures, emergency lighting with battery backup, certified switch gear
HVAC Equipment: Explosion-proof motors and fans, intrinsically safe temperature sensors, sealed ductwork penetrations
Control Systems: Explosion-proof control panels, intrinsically safe instrumentation, sealed conduit wiring
Mobile Devices: Intrinsically safe tablets like the Aegex10 IS Tablet with C1D1/ATEX Zone 1 certification
Process Equipment: Explosion-proof pumps and motors, intrinsically safe sensors, certified safety systems
Typical Features of a C1D1-Certified Room or Booth
Structural Elements: Interlocking steel panel walls, explosion-resistant doors with panic hardware, reinforced construction
Safety Systems: Explosion-proof lighting, gas monitoring with alarms, automatic fire suppression, emergency eyewash stations
Ventilation and Controls: High-capacity explosion-proof exhaust fans, makeup air systems, PLC controls with HMI interfaces

C1D1-certified equipment costs 20-30% more than standard alternatives, but prevents losses from accidents averaging $250,000 per incident.
Obtaining and Maintaining C1D1 Certification
Getting c1d1 certification requires the right team and typically takes 3-6 months. You need a licensed electrical engineer, certified equipment manufacturers, third-party testing laboratories, your local authority having jurisdiction (AHJ), and a qualified electrical contractor.
Step-by-Step Process to Achieve c1d1 certification
Step 1: Hazardous area classification study - A licensed engineer analyzes your facility to determine where dangerous conditions exist, considering flammable materials, normal operations, ventilation effectiveness, and equipment placement.
Step 2: Design development - Engineers create detailed plans showing equipment locations, electrical systems with conduit routing, ventilation layouts, and integrated safety systems.
Step 3: Equipment procurement - All equipment must carry proper c1d1 certification markings from recognized laboratories, with complete documentation including certificates, test reports, and installation instructions.
Step 4: Installation and testing - Qualified contractors follow NEC requirements for conduit sealing, manufacturer specifications, and local codes.
Step 5: Third-party inspection - Independent inspectors verify everything matches approved plans, checking certification markings, installation workmanship, and documentation.
Step 6: Final approval - AHJ issues operating approval with final inspection reports, as-built drawings, operation manuals, and training records.
How Often Must C1D1 Certification Be Renewed?
Annual inspections verify equipment functionality, visible certification markings, design specification compliance, and proper documentation of changes.
Major recertification every three years includes comprehensive system evaluation, updated classification studies, equipment testing verification, and personnel training updates.
Maintenance records must document all inspection reports, equipment maintenance activities, training updates, and system modifications. Good record-keeping proves maintained safety standards for insurance, regulators, and legal requirements.
Industry Applications, Benefits & Risks of Non-Compliance
C1d1 certification applies across multiple industries. Over 60% of North American oil and gas processing facilities contain C1D1 areas, including wellheads, processing units, and storage facilities.
Cannabis extraction drives major certification demand - over 70% of commercial extraction labs use hydrocarbon solvents requiring C1D1 classification for extraction booths and processing areas.
Chemical manufacturing, pharmaceutical production with solvent-based processes, and even some mortuary facilities handling preservation chemicals or flammable refrigerants need certification.
Scientific research on explosion prevention demonstrates how effective proper hazardous location practices prevent incidents.
Real-World Examples of C1D1 Success Stories
A Colorado cannabis facility invested in complete certified booth systems with explosion-proof ventilation, high air exchange rates, integrated gas detection, and intrinsically safe monitoring. Results: zero incidents over three years, full regulatory compliance, and reduced insurance premiums.
A Texas refinery upgraded to modern C1D1 standards, replacing electrical systems with explosion-proof alternatives and installing advanced gas detection. Outcome: 95% reduction in ignition-related incident risk and smooth regulatory inspections.
Financial & Safety Consequences of Skipping Certification
OSHA fines exceed $100,000 for hazardous location violations. Average accident costs hit $250,000 per incident, including property damage, business interruption, medical costs, and legal fees.
Insurance companies require certification proof before writing policies. Non-certified facilities face higher premiums, coverage exclusions, or policy cancellation.
Reputation damage affects customer confidence, employee recruitment, regulatory scrutiny, and community relations.
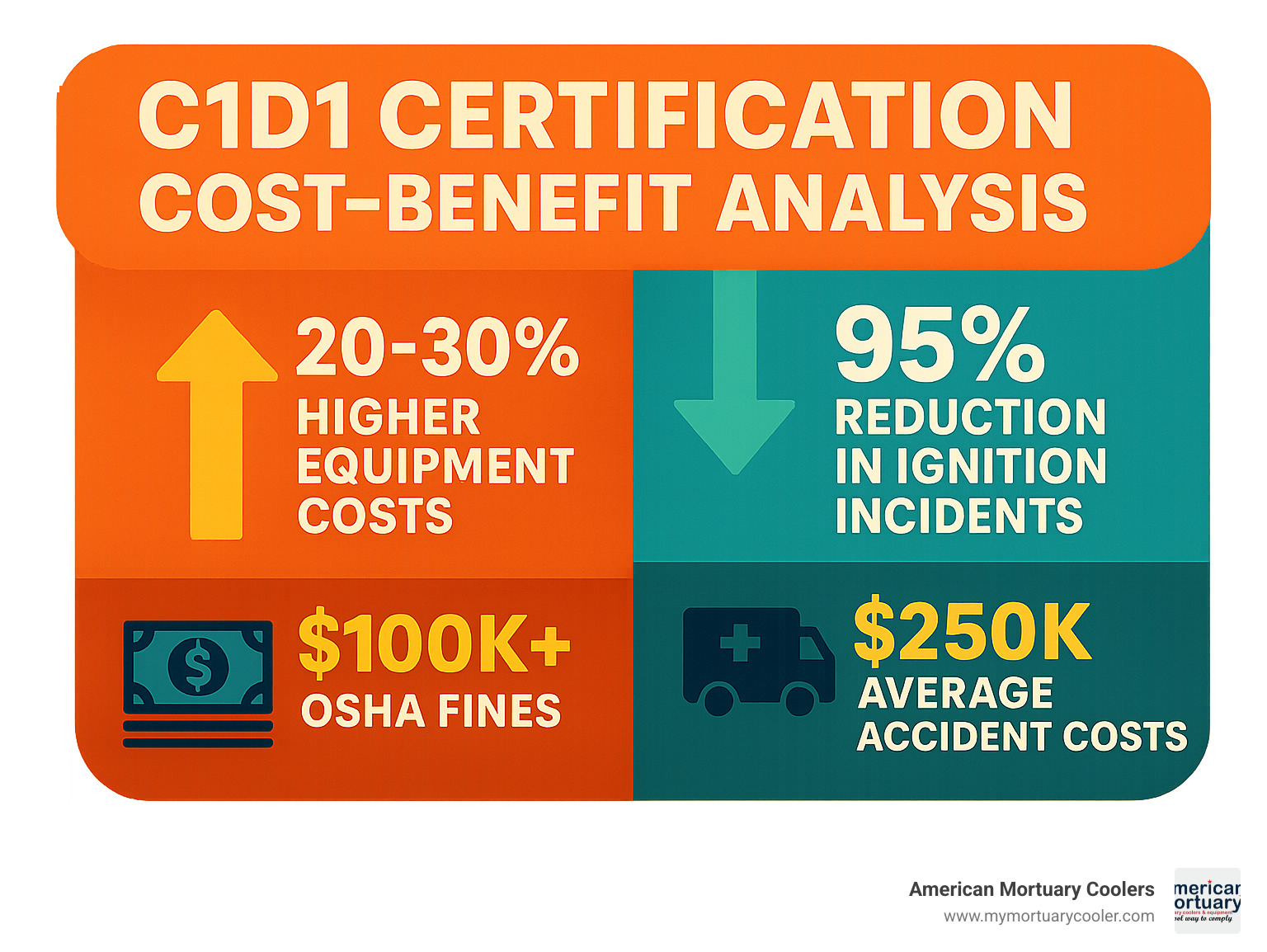
Proper certification costs 20-30% more than standard equipment but prevents $100,000+ fines, $250,000 accident costs, and potential business closure.
Frequently Asked Questions about C1D1 Certification
What documentation is required for a C1D1 inspection?
Inspectors need complete documentation including P&ID drawings showing equipment locations, equipment lists with certification markings, and hazardous area classification drawings mapping C1D1 zones.
Test reports prove system functionality through initial commissioning reports, ongoing maintenance records, and gas detection calibration certificates.
Administrative documentation includes training records showing personnel safety knowledge, emergency procedures, and incident reports demonstrating continuous improvement.
Can intrinsically safe equipment replace explosion-proof gear in C1D1 zones?
Yes, but with important considerations. Intrinsically safe equipment prevents problems by limiting energy below ignition levels, while explosion-proof gear contains explosions in heavy enclosures.
Energy-limiting design requires every component to stay below ignition thresholds even during two simultaneous faults. Approval scope is specific - equipment approved for Group D gases won't necessarily work with Group C gases.
System integration needs special barriers when connecting to regular control systems, and the entire circuit path must maintain intrinsic safety.
Who is qualified to perform C1D1 area classifications?
Licensed engineers with electrical licensing and hazardous location experience handle area classification studies. They must understand process chemistry, ventilation effectiveness, and electrical protection methods.
Certified inspectors from organizations like NICET and IAEI provide independent verification. Equipment manufacturers also certify inspectors on specific products.
The authority having jurisdiction gets final approval. Involve local fire marshals or electrical inspectors early in projects to prevent delays during final approval.
Conclusion
C1d1 certification creates workplaces where everyone goes home safely. This certification saves lives and protects businesses through proper safety standards.
Certified equipment costs 20-30% more than standard alternatives, but explosion-related accidents average $250,000 and OSHA fines exceed $100,000. The investment makes financial sense.
From our work at American Mortuary Coolers, we understand how overwhelming safety regulations feel. Whether running cannabis extraction, chemical processing, or handling flammable substances, c1d1 certification provides invaluable peace of mind.
The certification process follows a clear path: professional hazardous area classification study, qualified engineering design, certified equipment selection, qualified contractor installation, and third-party inspection.
Certification requires ongoing commitment through annual inspections and three-year recertification cycles. Successful facilities treat safety as continuous commitment, not a one-time hurdle.
Properly certified facilities see 95% reduction in ignition-related incidents compared to non-certified operations. This represents real people staying safe, businesses avoiding disasters, and communities protected from industrial accidents.
Whether in Johnson City, TN or Los Angeles, CA, c1d1 certification requires investment, planning, and ongoing attention. It delivers confidence that you've done everything possible to protect your people and operation.
Don't wait for incidents to force action. If your facility handles flammable substances under normal operating conditions, start certification today. Your workers, insurance company, and bottom line will benefit.
More info about commercial cooler repair services provides additional insights into maintaining certified equipment for optimal safety and performance.