Why Standardized Histology Dissection Categories Are Critical for Modern Pathology Labs
Histology dissection categories pdf resources provide essential classification frameworks that guide pathologists and laboratory technicians through proper specimen handlingfrom initial collection to final slide preparation. These standardized protocols ensure consistent processing across different specimen types, whether you are dealing with small skin biopsies, large tumor resections, or bone marrow samples that need specialized fixation.
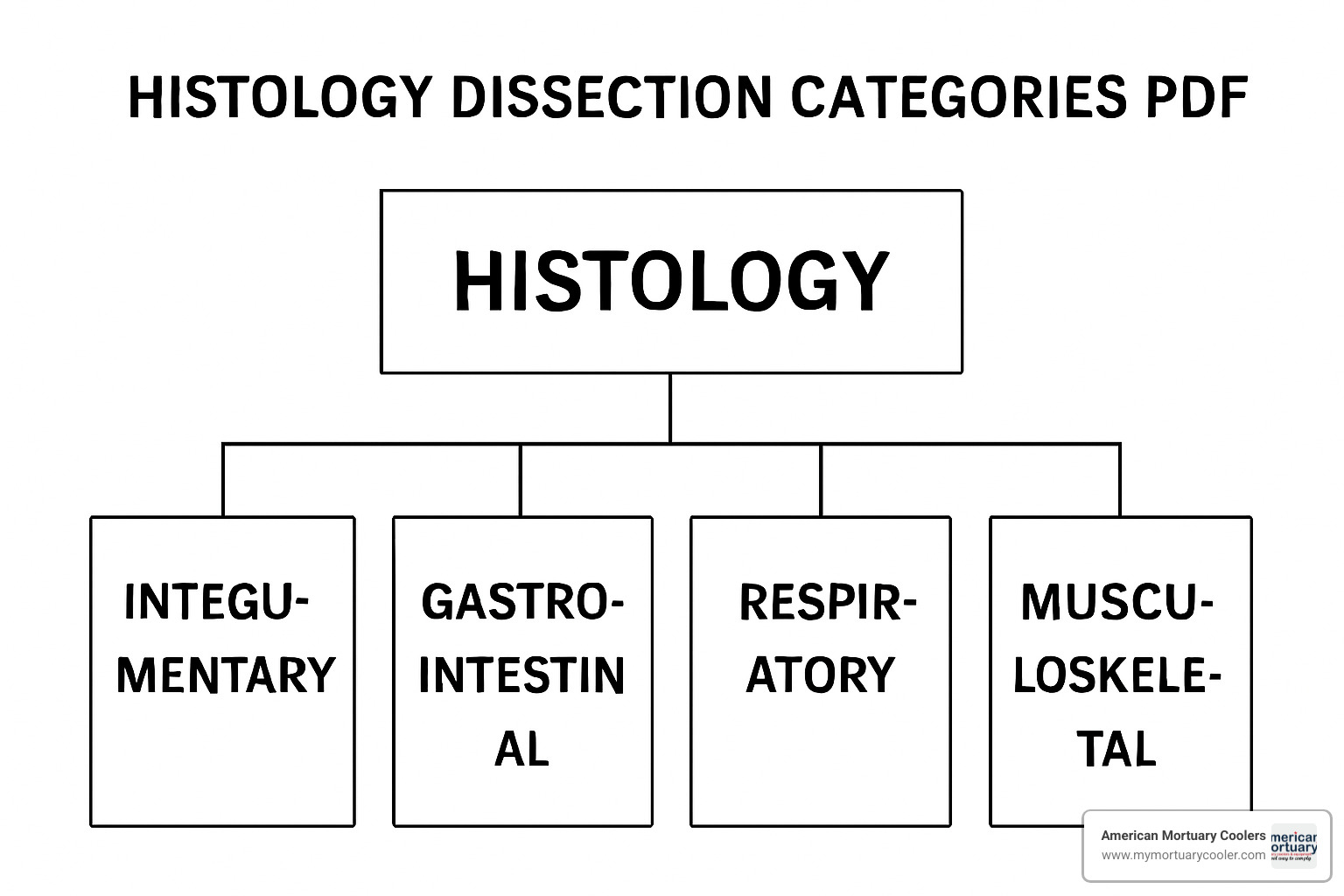
Main Histology Dissection Categories:
- Small Biopsies: skin punch, GI mucosa, needle core biopsies
- Large Resections: organ specimens, tumor margins, lymph-node dissections
- Bone & Calcified Tissue: specimens that require decalcification protocols
- Specimens for Ancillary Studies: molecular testing, microbiology, immunofluorescence
- Frozen Section Materials: intra-operative consultation specimens
- Autopsy Specimens: post-mortem tissue collection
The College of American Pathologists (CAP) estimates that specimen misidentification errors occur at approximately 1 in 1,000 cases, making standardized dissection protocols absolutely critical for patient safety.
These classification systems directly affect fixation ratios (151:1 fixative to tissue), processing times (672 hours for formalin), and section thickness limits (34 mm maximum) that determine diagnostic quality. Without proper categorization, laboratories risk compromising molecular studies, missing critical margins, or creating artifacts that obscure pathological findings.
At American Mortuary Coolers, we have seen first-hand how proper specimen handlingguided by comprehensive histology dissection categories pdf resourcescan streamline workflow and improve diagnostic accuracy.
Simple guide to histology dissection categories pdf terms:
Understanding Histology Dissection Categories PDF
Think of a histology dissection categories pdf as your laboratory's roadmap - it's the essential guide that helps pathologists and technicians steer the complex world of specimen processing. These classification schemes organize specimens by what they are and what they need.
A tiny skin punch biopsy gets completely different treatment than a large colon resection with suspicious margins. Small biopsies like mucosal samples can often be embedded whole, while large resections require systematic bread-loafing, careful margin inking, and strategic sampling to capture every diagnostic detail.
Why Laboratories Need a "Histology Dissection Categories PDF"
Specimen labeling errors account for up to 46% of all specimen-related errors in surgical pathology. This statistic explains why systematic approaches aren't just helpful - they're absolutely critical for patient safety.
A comprehensive histology dissection categories pdf acts like a safety net, ensuring that whether it's Monday morning or Friday afternoon, every specimen gets the attention it deserves. Standardized workflows mean less variability between different technicians and support CAP checklist compliance, helping laboratories sail through accreditation inspections.
Training new staff becomes infinitely easier when you have clear, written protocols. The regulatory landscape keeps evolving too, with CAP and NSH guidelines revised every two years, making downloadable PDF resources essential for staying current.
Core Category Framework Inside the histology dissection categories pdf
A well-structured classification system follows a logical hierarchy starting with primary sections for routine surgical specimens, then branches into subcategories for specialized handling requirements.
The primary categories include routine surgical specimens that follow standard fixation and processing, urgent frozen section materials that need 20-minute turnaround times, and decalcification required specimens like bone, teeth, and calcified tissues. Ancillary studies get their own category because they require fresh tissue allocation for molecular testing, microbiology cultures, or research protocols.
Size matters too. Minute specimens measuring 3mm or less get embedded entirely, small biopsies between 3mm and 1cm might need bisection, and large specimens over 5cm require systematic sectioning, multiple cassettes, and photographic documentation.
Pre-Analytical Workflow & Specimen Management
The pre-analytical phase - from specimen collection until it reaches the grossing station - is where most laboratory errors occur. Patient identification sits at the heart of specimen safety, requiring at least two independent identifiers linked to each specimen.
Container labeling requires waterproof labels on the container body, never on the lid. Chain of custody documentation becomes critical for specimens with potential legal implications, while cold ischemia time directly impacts tissue quality, particularly for molecular testing.
Collection, Labeling & Transport Best Practices
The two-identifier verification system creates multiple checkpoints for catching errors at bedside collection and laboratory accessioning. Barcode and RFID tracking systems eliminate handwriting errors, though labels must withstand formalin exposure and processing solvents.
Leak-proof containers maintain specimen integrity during transport and must comply with biohazardous material shipping regulations, including proper labeling and documentation for specimens traveling between facilities.
Fixation Protocols Across Dissection Categories
Ten percent neutral buffered formalin remains the workhorse of surgical pathology, providing excellent morphological preservation with a magic ratio of 15-20 parts fixative to 1 part tissue. The 6-72 hour fixation window is particularly critical for hormone receptor testing in breast cancer cases.
Special fixatives serve specific purposes: Bouin's solution provides superior nuclear detail for testicular biopsies, while formic acid-based decalcifiers gently remove calcium from bone specimens without harsh morphological damage.
| Specimen Type | Preferred Fixative | Fixation Time | Special Considerations |
|---|---|---|---|
| Routine surgical | 10% NBF | 6-72 hours | 15-20:1 ratio |
| Testicular biopsy | Bouin's solution | 2-4 hours | Superior nuclear detail |
| Bone specimens | 5-10% formic acid | 1-10 days | Gentle decalcification |
Minimizing Artifacts Before Grossing
Artifact prevention starts in the operating room. Thermal injury from electrocautery devices can obscure diagnostic features, especially at surgical margins. Crush artifacts result from excessive pressure during handling, while drying artifacts develop when specimens sit exposed to air before fixation.
More info about histology supplies can help laboratories maintain the tools needed for optimal specimen handling.
Gross Dissection Techniques by Category
Gross dissection transforms three-dimensional specimens into precise sections ready for microscopic examination. Orientation using anatomic landmarks and surgeon-placed orientation sutures helps read each specimen's story correctly.
Photographic documentation before and after dissection provides invaluable reference materials and quality assurance evidence. Inking margins on completely dry specimens prevents ink run-off that could turn negative margins into false positives. Slice thickness must stay within 3-4mm for proper processing.
Small Biopsy Workflows (Skin Punch, GI Mucosa) — histology dissection categories pdf Showcase
Small biopsies measuring less than 0.5 cm require careful handling to prevent tissue loss. The embed-in-toto approach works best, submitting specimens entirely in specialized biopsy cassettes designed to prevent tissue loss.
Color-coded triage systems improve workflow management - pink cassettes for small biopsies, green for urgent cases, white for standard specimens. Tissue bags or filter paper prevent tiny fragments from disappearing during processing.
Large Organ & Tumor Resections
Large specimens require systematic bread-loafing technique with parallel cuts at regular intervals. Margin assessment often determines whether patients need additional surgery, making perpendicular sections through margins critical for precise distance measurements.
Lymph node search requires patience and systematic technique, with specific minimum numbers needed for staging - typically 12 lymph nodes for colorectal specimens and 15 for gastric resections.
More info about forceps types can help select the right instruments for delicate lymph node dissection.
Bone & Decalcified Specimens
Bone specimens require decalcification before routine processing. 5-10% formic acid provides controlled decalcification with minimal morphological damage, typically completing in 1-10 days. EDTA-based chelating agents offer gentler decalcification but require longer processing times.
Endpoint testing ensures complete decalcification without over-processing through physical methods like palpation and needle penetration, or radiographic assessment.
Specimens for Ancillary Studies
Modern pathology increasingly relies on ancillary studies requiring fresh or specially processed tissue. Effective tissue triage allocates appropriate portions for each study while preserving adequate material for routine histology.
Molecular testing requires high-quality DNA and RNA, demanding immediate freezing or rapid fixation in specialized preservatives. Cold ischemic time should be minimized and documented.

Quality Assurance, Documentation & Regulatory Compliance
Quality assurance in histology starts with solid accessioning procedures that verify specimen identity and evaluate fixation adequacy. Laboratory Information System (LIS) integration eliminates handwriting errors while barcode scanning prevents specimen mix-ups.
The regulatory landscape includes ISO 15189 standards, plus CAP and CLIA regulations that specify staff qualifications, proficiency testing, and error response procedures.
QA Measures to Prevent Misidentification
The "one specimen rule" prevents catastrophic mix-ups by allowing only one specimen at the cutting station at any time. Dual verification systems create two independent checkpoints confirming specimen identity during accessioning and at the grossing station.
Color-coded cassette systems provide visual cues - green for urgent specimens, pink for tiny biopsies, white for routine cases. Incident reporting systems capture near-misses and actual errors, focusing on fixing system problems rather than assigning blame.
Documentation Essentials for Each Dissection Category — histology dissection categories pdf Templates
Gross descriptions serve as legal documents capturing what pathologists see and how they sample specimens. Block keys map each tissue cassette to its precise location within the original specimen, proving essential for additional sampling or quality reviews.
Slide indexing systems track specimens through their entire journey, while photographic archiving provides permanent visual records integrated with laboratory information systems.
More info about curved Mayo scissors and other dissection instruments helps ensure proper technique and documentation.
Storage, Retention & Final Disposal
Fixed tissue archives need controlled environmental conditions to prevent deterioration over decades. Paraffin blocks represent the permanent archival form, requiring organized storage with barcode tracking and sometimes automated retrieval systems.
Digital scanning technology creates virtual slide archives providing instant access while preserving original glass slides. Biohazard waste disposal follows strict regulatory guidelines with documented chain of custody through final destruction.
Meeting CAP & CLIA Requirements
CAP checklist items address every laboratory operation aspect, including specific requirements for gross dissection procedures and quality assurance measures. Proficiency testing programs assess laboratory performance against established standards.
Corrective action procedures address problems through root cause analysis, while external quality assurance programs provide independent performance assessment and benchmarking.
Frequently Asked Questions about Histology Dissection Categories PDF
When I talk with laboratory professionals, the same questions about histology dissection categories pdf resources come up repeatedly. These practical concerns affect daily workflow and patient care.
What are the main dissection categories recognized by CAP?
The College of American Pathologists has developed a comprehensive framework that most laboratories use as their foundation.
Small biopsies include skin punch biopsies, GI mucosal samples, and needle core biopsies typically 1cm or smaller. Most can be submitted entirely without sectioning, often in pink-coded cassettes.
Large resections are organ specimens and tumor resections requiring systematic bread-loafing, careful margin assessment, and strategic sampling. These demand organization - proper orientation, photographic documentation, and detailed block mapping.
Bone and calcified tissues present unique challenges. CAP recommends 5-10% formic acid for controlled decalcification with careful endpoint testing.
Specimens for ancillary studies have become increasingly important as molecular testing expands. Fresh tissue allocation requires immediate attention and specialized handling.
Frozen section materials demand immediate processing with 20-minute turnaround expectations when surgeons are waiting in the operating room.
How does specimen size influence cassette submission guidelines?
The fundamental rule is that tissue thickness must not exceed 3-4mm for adequate fixation and processing, regardless of specimen size.
Minute specimens measuring 3mm or less can be submitted entirely without sectioning, often requiring tissue bags to prevent loss during processing.
Small biopsies between 3mm and 1cm may need bisection if too thick, while maintaining proper orientation for complete microscopic examination.
Large specimens over 5cm demand comprehensive sampling strategies with multiple cassettes, detailed block mapping, and photographic documentation.
The 15-20:1 fixative-to-tissue ratio applies regardless of specimen size, though larger specimens may require fixative changes if the solution becomes cloudy.
Where can I download an accredited histology dissection categories pdf?
Finding reliable resources requires knowing where to look and what to trust. Not all resources are created equal.
The College of American Pathologists remains the gold standard for US laboratories. Their comprehensive tissue pathways and checklists are available through the member portal and updated every two years.
The Royal College of Pathologists provides detailed tissue pathways for specific organ systems, with evidence-based recommendations graded from A-D.
The National Society for Histotechnology publishes practical guidelines specifically for histotechnology professionals, bridging the gap between high-level pathology protocols and day-to-day laboratory operations.
When selecting resources, ensure they align with your laboratory's accreditation requirements - whether CAP, CLIA, or ISO 15189. The best histology dissection categories pdf is the one your laboratory actually uses consistently.
Conclusion
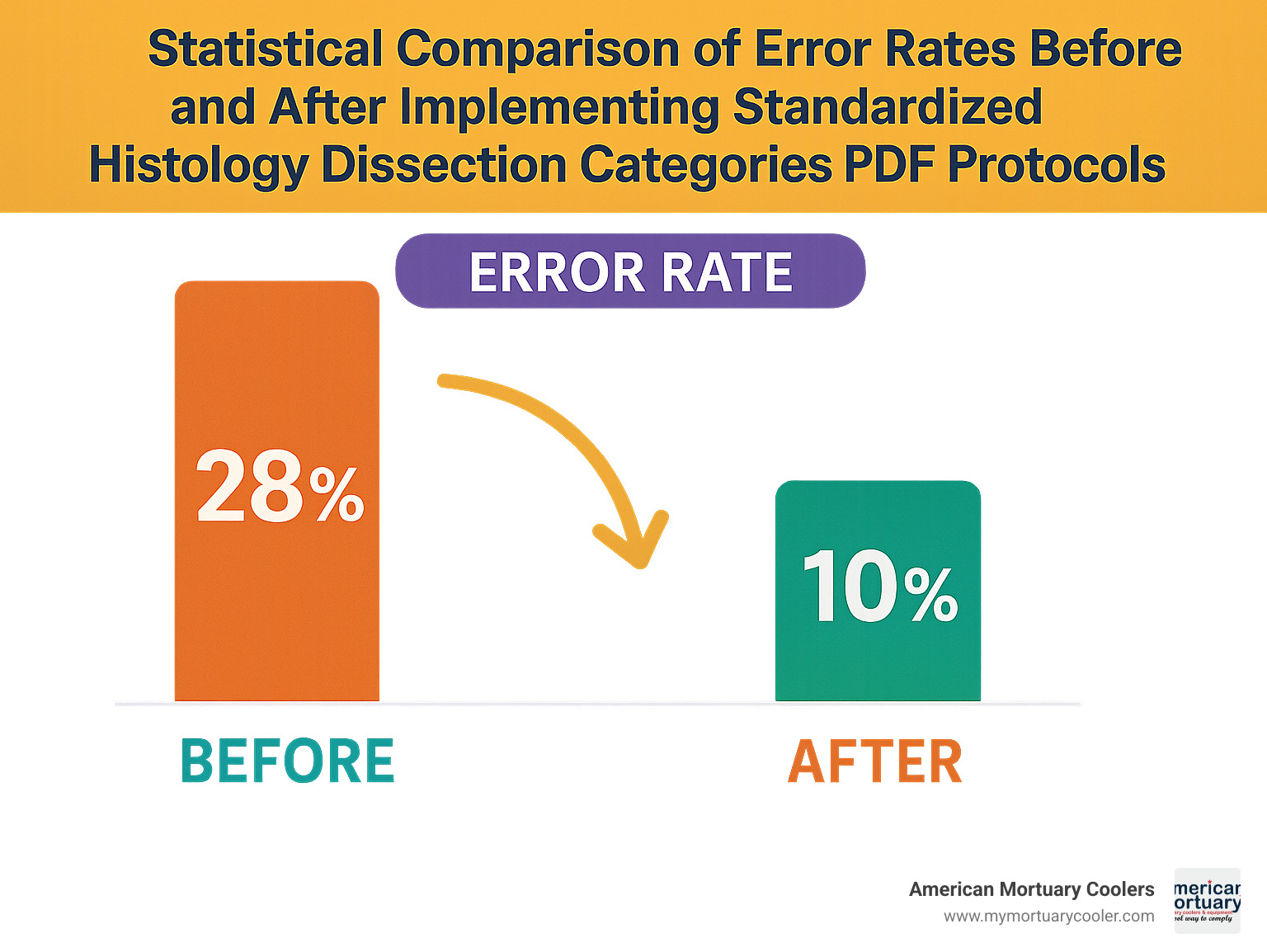
When you implement comprehensive histology dissection categories pdf resources in your pathology lab, you're changing how your entire team approaches specimen handling. These standardized protocols tackle that concerning 1-in-1,000 specimen misidentification error rate while ensuring every specimen gets careful attention regardless of processing time.
The real magic happens when your lab moves from "that's how we've always done it" to systematic, quality-driven workflows. Labs that make this shift consistently report fewer processing problems, faster turnaround times, and confident staff handling complex specimens.
Here at American Mortuary Coolers, we've learned that specimen integrity is a team effort. It starts with proper collection, continues through our specialized cooling equipment, and extends to your grossing station. Every link in that chain matters.
Whether you're running a hospital lab or managing a busy reference facility, the fundamentals stay the same. Proper specimen identification can't be compromised. Appropriate fixation protocols make or break downstream processing. Systematic dissection techniques turn chaos into clarity. Comprehensive documentation protects patients, staff, and your lab's reputation.
We've watched laboratories from Johnson City to Los Angeles achieve remarkable improvements after implementing standardized dissection protocols. The secret isn't treating your histology dissection categories pdf like a dusty manual. These resources work best when they become living guides that grow with your lab's needs.
The most successful labs understand that standardization doesn't mean rigidity. It means having solid foundations that let you innovate safely. When your basic processes are rock-solid, your team can focus on advancing patient care instead of firefighting preventable problems.
For labs ready to strengthen their specimen management from collection through storage, more info about morgue freezers and our other specialized equipment can provide the infrastructure backbone supporting everything else you're accomplishing.
The future belongs to pathology labs that accept smart standardization while staying nimble enough to adopt new technologies. Histology dissection categories pdf resources give you that perfect balance - the structure you need with the flexibility to keep improving, ensuring patient safety remains at the heart of everything you do.