Introduction
Understanding what is regional pricing starts with a simple truth: not every dollar stretches the same way in New York as it does in Nashville, Nairobi, or New Delhi. Regional pricing—sometimes called zone pricing, geographic pricing, or price localization—is a strategy businesses use to set different prices for the same product or service depending on where the buyer is located.
Core Definition of “what is regional pricing”
At its heart, regional pricing is differential pricing. We adjust prices up or down for a product based on factors like:
- Purchasing power parity (PPP): The average amount people can spend in a given region.
- Local taxes and duties: Sales tax, VAT, tariffs, or import fees.
- Currency exchange rates: Fluctuations in value compared to the seller’s home currency.
- Logistics and shipping costs: The cost of delivering goods to far-flung or hard-to-reach areas.
- Market demand and competition: If there’s more competition or higher/lower demand in a region, prices may change accordingly.
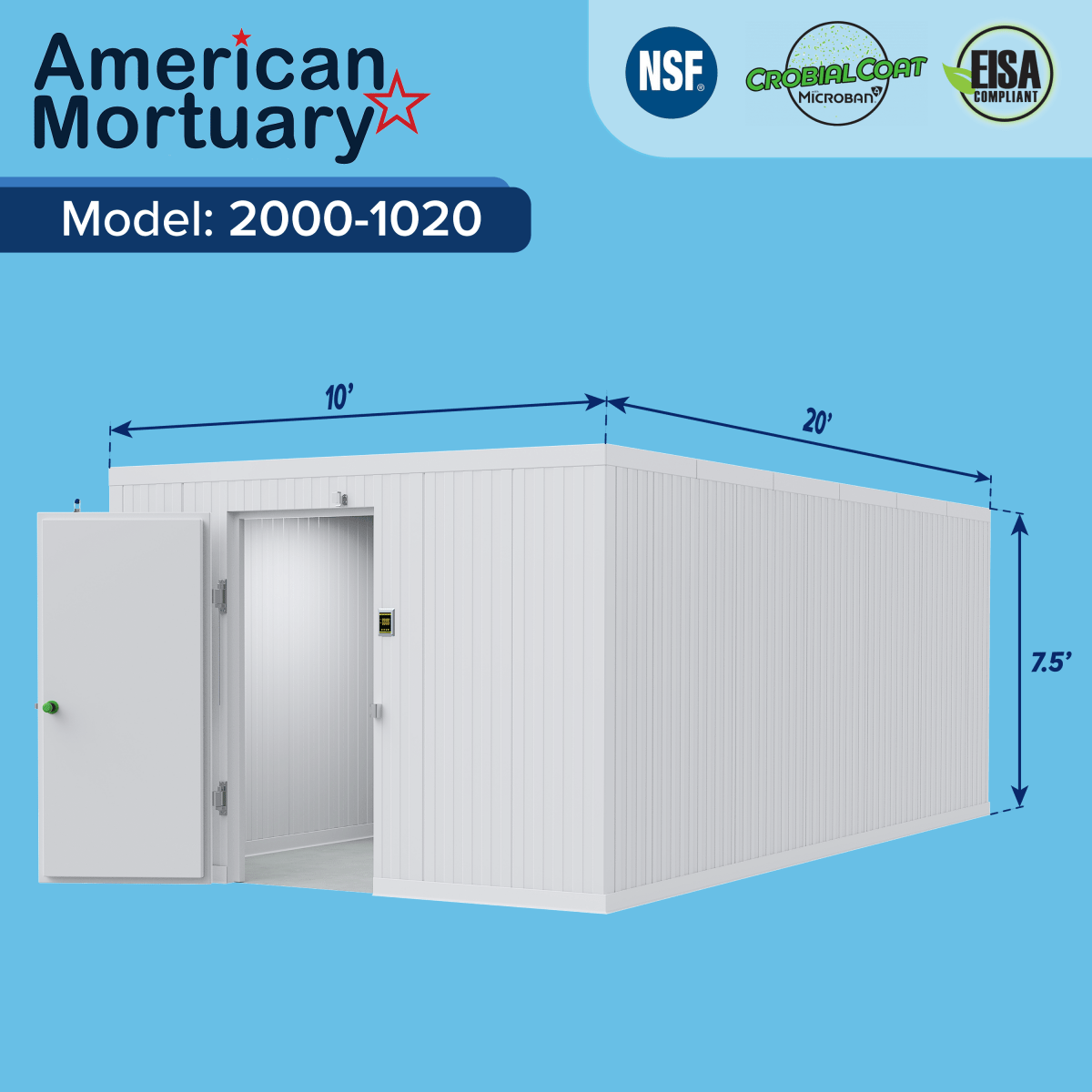
This is not just about “charging what the market will bear.” It’s about making the same product accessible and fairly priced in each local context—whether you’re selling mortuary coolers in Atlanta or software subscriptions in Argentina.
Mechanisms Behind “what is regional pricing” in Digital Stores
Let’s peek under the digital hood for a moment. In online storefronts (like app stores, gaming platforms, or e-commerce shops), regional pricing is driven by:
- Geo-IP detection: The website or app identifies your location using your IP address or billing info.
- Automatic vs. manual price tiers: Some platforms auto-calculate prices based on a formula (PPP, exchange rates, etc.), while others allow merchants to set prices for each region.
- Geo-blocking and payment region locks: To prevent cross-border arbitrage (people pretending to be in a cheaper region), some stores restrict access by region and payment method.
| Feature | Automatic Price Tiers | Manual Price Setting |
|---|---|---|
| Who sets the price? | Platform algorithm (e.g., PPP, CPI, exchange) | Merchant or publisher for each region |
| Speed of updates | Frequent (reflects currency/tax changes fast) | As often as merchant reviews them |
| Control | Limited for merchants | Full—can tailor to strategy |
| Example | Spotify, Roblox, Google Play | Steam, Epic Games Store, SaaS vendors |
In the mortuary industry, many equipment providers now use similar systems—factoring in regional delivery costs, state taxes, and local market demand when quoting prices to funeral homes.