Why Understanding the R404 Chart is Critical for Refrigeration Success
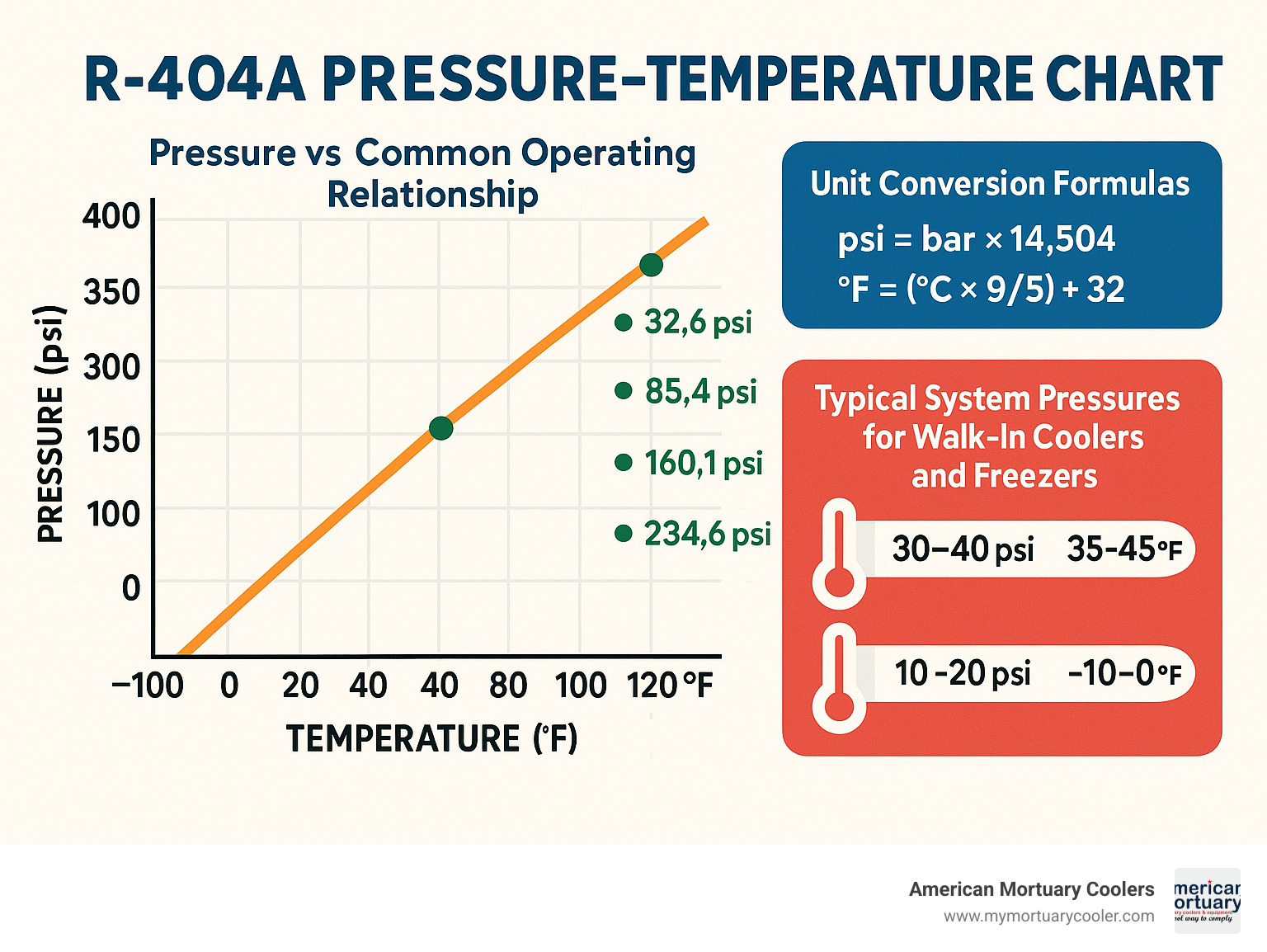
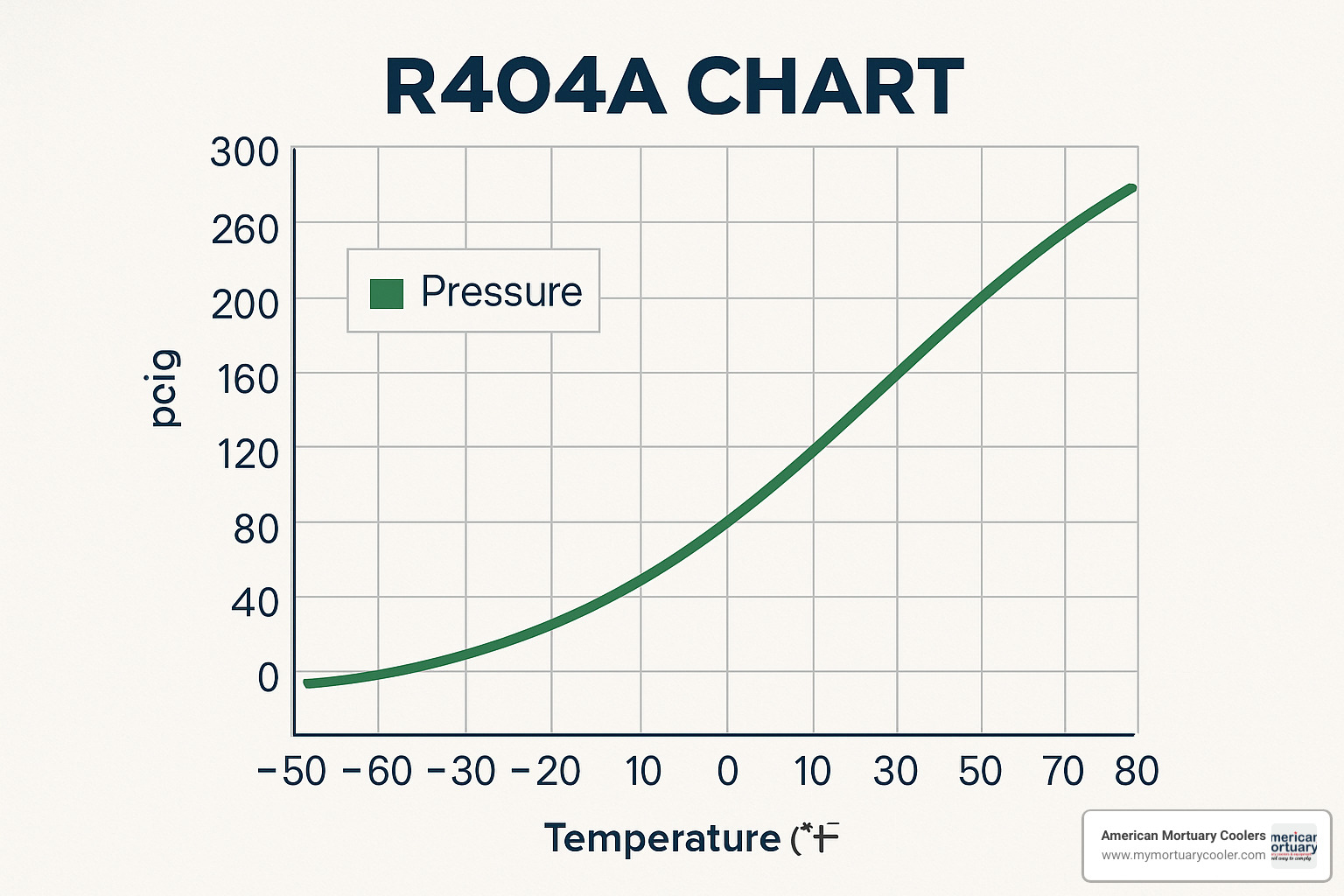
The r404 chart is a pressure-temperature reference table that shows the exact relationship between R-404A refrigerant pressure and temperature at saturation conditions. This chart is essential for proper system charging, diagnostics, and troubleshooting in commercial refrigeration applications.
Quick R404 Chart Reference:
- At 0°F: 32.6 psi
- At 40°F: 85.4 psi
- At 80°F: 160.1 psi
- At 100°F: 234.6 psi
- Boiling Point: -51.88°F at atmospheric pressure
- Critical Temperature: 161.7°F
- Critical Pressure: 540.8 psi
R-404A is a hydrofluorocarbon (HFC) blend consisting of 44% R-125, 4% R-134a, and 52% R-143a. It's widely used in low and medium-temperature commercial refrigeration including walk-in coolers, freezers, supermarket display cases, and mortuary cooling systems.
The r404 chart becomes your diagnostic compass when troubleshooting refrigeration issues. By measuring system pressure and comparing it to chart values, you can quickly identify problems like undercharge, overcharge, or mechanical failures that affect system performance.
However, R-404A faces regulatory pressure due to its high Global Warming Potential (GWP) of 3,922. The EPA's AIM Act is phasing down high-GWP refrigerants, making understanding of alternative refrigerants and retrofit procedures increasingly important for technicians.
I'm Mortuary Cooler, a national-level mortuary cooler supplier with experience in commercial refrigeration systems that rely on accurate r404 chart interpretation for proper operation. My background includes designing and servicing custom mortuary cooling solutions where precise temperature control is critical for maintaining product integrity.
Related content about r404 chart:
Understanding R-404A Refrigerant
When you're working with commercial refrigeration systems, R-404A is probably one of the most reliable refrigerants you'll encounter. At American Mortuary Coolers, we've watched this workhorse perform flawlessly in our custom mortuary coolers for years, maintaining precise temperatures when it matters most.
This isn't just any refrigerant - it's a carefully crafted blend of 44% R-125, 4% R-134a, and 52% R-143a. Think of it as a recipe that creates the perfect balance for low and medium-temperature applications. Whether you're servicing walk-in freezers, supermarket display cases, or specialized mortuary equipment, R-404A delivers consistent performance.
Here's what makes R-404A environmentally interesting: it has an Ozone Depletion Potential (ODP) of 0, which means it won't harm the ozone layer. That's why it became such a popular replacement for older CFC and HCFC refrigerants. But there's a catch - its Global Warming Potential (GWP) of 3,922 is now causing regulatory headaches under the EPA's HFC phase-down program.
The numbers tell the story of why R-404A works so well in freezer applications. With a boiling point of -51.88°F at atmospheric pressure, it's perfectly suited for those deep-freeze temperatures. The critical temperature of 161.7°F gives you excellent performance even when ambient temperatures climb during hot summer days.
Safety-wise, R-404A carries a Safety Class A1 rating. This means it's non-toxic and non-flammable under normal conditions - something you definitely want when working in commercial installations where safety is paramount.
One thing that trips up some technicians is the oil requirement. R-404A systems must use polyolester (POE) oil. We've seen too many compressor failures over the years from technicians who didn't pay attention to this detail. The synthetic POE lubricant isn't optional - it's essential for proper compressor operation and system longevity.
Key Properties Every Technician Should Know
The physical properties of R-404A aren't just numbers on a spec sheet - they're practical details that affect how you work with this refrigerant every day. The molecular mass of 97.6 g/mol influences how the refrigerant behaves during charging and recovery operations, affecting everything from evacuation times to charging rates.
When you see that critical pressure of 540.8 psi, remember this represents the absolute maximum pressure R-404A can reach, regardless of how hot it gets. This knowledge helps you understand system limitations and troubleshoot high-pressure situations more effectively.
The orange color coding on R-404A cylinders isn't just for looks - it's your first line of defense against accidentally mixing refrigerants. We always tell our technicians to check that orange cylinder twice before connecting anything. One wrong move with refrigerant mixing can turn a simple service call into an expensive system replacement.
Here's something that makes R-404A easier to work with: it has negligible temperature glide. Unlike some newer refrigerant blends that can have significant temperature differences during phase change, R-404A stays relatively constant. This means your r404 chart readings are more straightforward, and charging procedures are less complicated.
As a substitute for R-22 in many applications, R-404A typically runs at higher pressures. This pressure difference requires careful attention to system components, especially expansion valves and pressure controls, when retrofitting older R-22 systems.
Mastering the R404 Chart
Think of the r404 chart as your trusted companion in the field - it's the bridge between what your gauges are telling you and what's actually happening inside the refrigeration system. This pressure-temperature chart reveals the exact relationship between R-404A's pressure and temperature when the refrigerant is at saturation conditions, where liquid and vapor coexist in perfect balance.
Here's where things get interesting with refrigerant blends like R-404A. Unlike pure refrigerants, blends have bubble and dew points that behave slightly differently. The bubble point is when you first see vapor bubbles forming as you heat the liquid, while the dew point is when the first drops of liquid appear as you cool the vapor. The good news? R-404A has negligible temperature glide, so these two points are practically identical - making your job much easier.
Most professional r404 charts come with dual units that display temperature in both Fahrenheit and Celsius, plus pressure readings in both psig and bar. This isn't just convenience - it's a real time-saver when you're working with equipment from different manufacturers or dealing with international specifications.
The saturation table is where the magic happens. This is your reference point for determining whether your system is running with proper superheat and subcooling. When system pressures match the chart values at measured temperatures, you know you're in the ballpark. When they don't, you've found your starting point for diagnosis.
For a deeper dive into reading these charts effectively, our Quick Start Guide to R404 Pressure Temperature Charts walks through real-world examples that can save you hours of troubleshooting.
How to Read an R404 Chart Step-by-Step

Reading an r404 chart correctly separates the pros from the rookies. After years of working with mortuary coolers where precise temperature control is absolutely critical, I've developed a foolproof approach that works every time.
Start by measuring the actual temperature at your point of interest using a calibrated thermometer. Whether you're checking the evaporator outlet or condenser inlet, accuracy here sets the foundation for everything else. Next, take your pressure reading with properly calibrated manifold gauges - and yes, calibration matters more than you might think.
Now comes the chart work. Locate your measured pressure on the pressure column, then find the corresponding saturation temperature. This is where the refrigerant wants to be at that pressure. The difference between your actual measured temperature and this saturation temperature tells the whole story.
For superheat calculation, subtract the saturation temperature from your actual measured temperature. If you're seeing 8-12°F of superheat, you're typically in good shape. Too little superheat might mean liquid flood-back is threatening your compressor. Too much could indicate an undercharged system or a starved evaporator.
Subcooling checks work similarly but in reverse. Compare your liquid line temperature to the saturation temperature at condensing pressure. This tells you how much cooling the refrigerant received after condensing, which affects system capacity and efficiency.
The beauty of this systematic approach is that it quickly points you toward the problem. When your measurements don't align with chart values, you've found your diagnostic starting point.
Using the R404 Chart for Charging & Diagnostics
Charging R-404A systems requires liquid charging to prevent the blend components from separating - a process called fractionation that can seriously mess up system performance. The r404 chart becomes your guide during charging, helping you hit those target superheat values of 8-12°F that most commercial refrigeration systems need.
When you're facing low suction pressure faults, the chart helps you distinguish between a simple undercharge and more complex mechanical issues like expansion valve problems. High head pressure situations become clearer when you compare actual condensing pressures to what the chart says they should be at current ambient conditions.
Here's something we've learned from servicing mortuary coolers across the country: subcooling checks are just as important as superheat measurements. Proper subcooling ensures you're getting full system capacity and helps prevent flash gas formation in the liquid line. The chart makes these calculations straightforward and reliable.
For technicians who want to take their diagnostic skills to the next level, tools like the HVAC Buddy Charging & Diagnostic app incorporate pressure-temperature relationships for more precise calculations. But remember - understanding the fundamentals of how to read the chart manually will always be your most valuable skill.
Field Applications & Typical Pressures
When you're working on commercial refrigeration systems day in and day out, you start to notice patterns. After years of installing and servicing mortuary cooling systems across Tennessee, Georgia, Illinois, and beyond, we've seen how R-404A behaves in real-world conditions - and it's remarkably consistent once you know what to look for.
Walk-in coolers are probably where you'll encounter R-404A most often. These systems typically run with suction pressures between 15-25 psig, which translates to evaporator temperatures around 0-10°F on your r404 chart. This pressure range hits that sweet spot where you get solid refrigeration capacity without making your compressor work overtime.
Morgue freezers tell a different story because they need to maintain much lower temperatures than your typical grocery store freezer. We see suction pressures in the 5-15 psig range for these applications, corresponding to evaporator temperatures of -10 to 0°F. It's exactly what you need for proper preservation, but it means your system components have to work harder.
The discharge side is where things get interesting because it changes with the weather. On a 90°F day, expect discharge pressures between 200-270 psig. When summer heat waves hit, those pressures climb even higher, which is why keeping condensers clean and ensuring good airflow isn't just maintenance - it's survival for your system.
Supermarket refrigeration racks present their own challenges. These large systems often run multiple evaporators at different temperature levels, so you might see a wider range of operating pressures on the same rack. The key is understanding what each circuit is supposed to do and checking pressures accordingly.

Converting Units Quickly on the Job
Nothing slows down a service call like fumbling with unit conversions. Whether you're dealing with equipment specs in metric units or trying to communicate with a customer who thinks in Celsius, having quick conversion methods saves time and prevents mistakes.
Temperature conversions are straightforward once you memorize the formulas. °F to °C: subtract 32, then multiply by 5/9. Going the other way? °C to °F: multiply by 9/5, then add 32. Most of us just remember that 32°F equals 0°C and 212°F equals 100°C, then estimate from there for quick checks.
Pressure conversions come up when you're working with imported equipment or consulting international technical documents. To convert psig to bar, divide by 14.504. To convert bar to psig, multiply by 14.504. Many technicians round this to 14.5 for quick field calculations - it's close enough for most diagnostic work.
Don't forget about psia versus psig - absolute pressure includes atmospheric pressure (14.7 psi), while gauge pressure doesn't. To convert psia to psig, subtract 14.7. This matters when you're reading technical specifications or working with vacuum measurements.
Our Practical Guide to Finding a PT Chart for R404A Refrigerant includes handy conversion tables you can keep in your truck for quick reference.
Bubble vs Dew Explained on the R404 Chart
Here's where R-404A makes your life easier compared to some of the newer refrigerant blends. Understanding bubble and dew points might sound complicated, but with R-404A's minimal temperature glide, you're dealing with a pretty forgiving refrigerant.
The bubble point is when your saturated liquid starts to boil and create vapor bubbles. The dew point is the opposite - when saturated vapor starts to condense back into liquid drops. With most refrigerants, these temperatures are different, but R-404A's temperature glide is less than 1°F, so bubble and dew points are nearly identical.
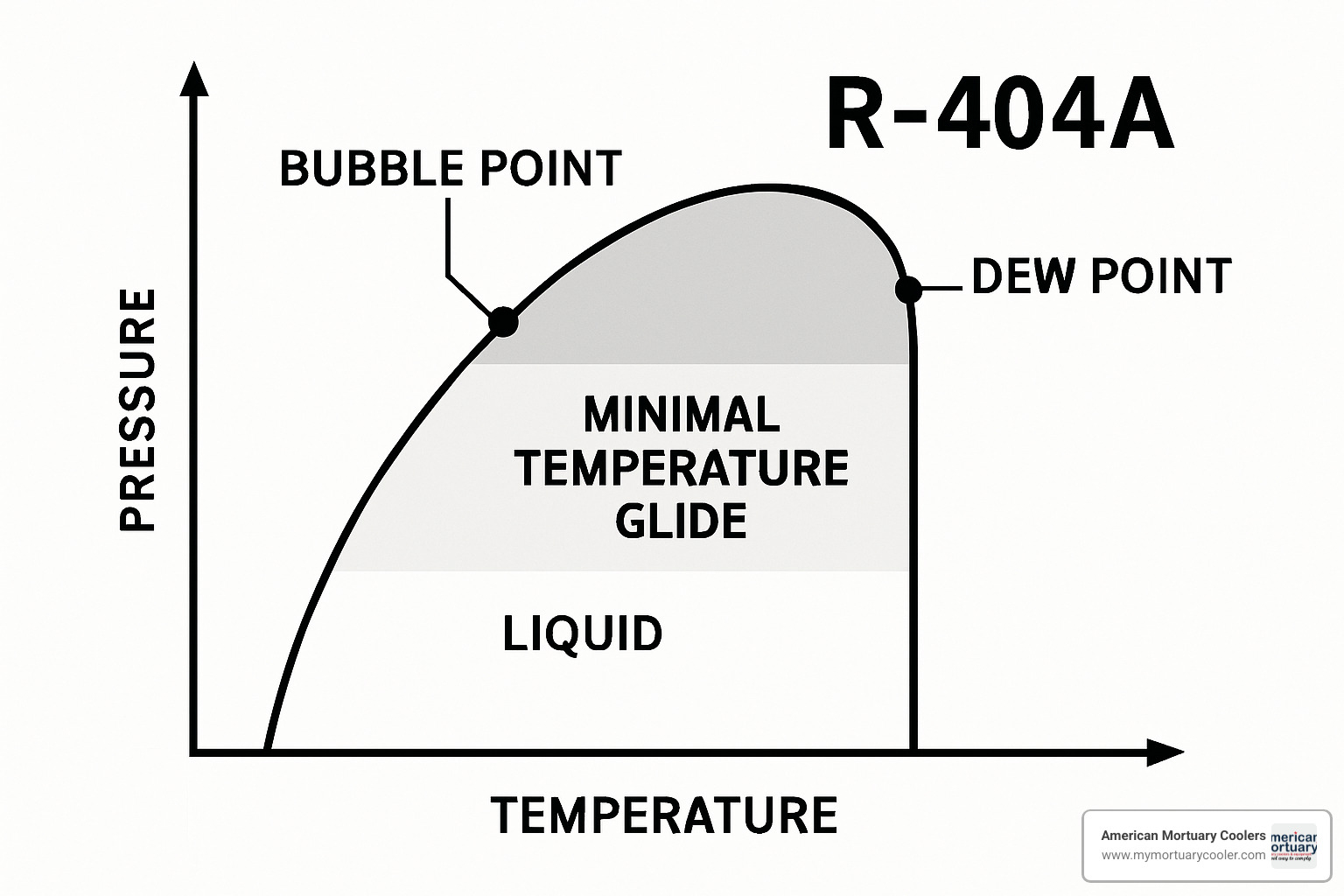
This minimal glide makes TXV adjustment more straightforward. When you're setting superheat, you don't have to worry about significant temperature differences between bubble and dew points affecting your calculations. Your r404 chart readings will be consistent and predictable.
Charging accuracy becomes crucial with any blended refrigerant, even one with minimal glide like R-404A. Always charge as a liquid from the cylinder to maintain proper blend ratios. Even small amounts of vapor charging can throw off the blend composition over time, leading to performance issues that are hard to diagnose.
Alternatives, Regulations & Environmental Considerations
The world of R-404A refrigerant is changing fast, and frankly, it's about time. At American Mortuary Coolers, we've been watching these regulatory shifts closely because they directly impact the systems we design and service. The EPA's AIM Act is reshaping the refrigeration landscape by mandating a dramatic phase-down of HFC production and consumption to just 15% of baseline levels by 2036.
This isn't just regulatory paperwork - it's a fundamental shift that affects R-404A availability and cost. We're already seeing price increases and supply constraints that make understanding alternative refrigerants essential for anyone planning long-term system investments.
The high Global Warming Potential of R-404A (GWP 3,922) is what's driving this change. The good news? We have viable alternatives like R-448A (GWP 1,274) and R-449A (GWP 1,282) that deliver similar performance while dramatically reducing environmental impact. These aren't perfect drop-in replacements, but they're close enough to make retrofitting practical.
Converting from R-404A to alternative refrigerants requires careful planning and execution. The process starts with establishing baseline system performance data so you know what normal operation looks like. Next comes complete refrigerant recovery - and we mean complete. Any remaining R-404A will contaminate the new refrigerant and affect performance.
Fresh filter driers and thorough leak checks are non-negotiable during retrofits. The system needs proper evacuation to deep vacuum levels before charging with the alternative refrigerant. Most conversions require 95-105% of the original charge weight, but this varies by refrigerant type. Finally, expansion valves and pressure controls often need adjustment to optimize performance with the new refrigerant properties.
Safety classifications matter more than ever. R-404A carries an A1 rating (non-toxic, non-flammable), which makes it relatively safe to work with. Some alternatives have A2L ratings (mildly flammable), requiring additional safety measures including leak detection systems and modified installation practices per ASHRAE 15 standards.
Recovery and recycling of R-404A becomes critical as supplies tighten. Proper recovery equipment rated for at least 300 psig is essential for safe handling. We always emphasize proper PPE including safety glasses and gloves when working with pressurized systems - refrigerant under pressure can cause serious injury.
For the latest regulatory updates, check the EPA's HFC reduction program frequently. These rules change faster than most technicians expect.
Comparing R-404A to R-22 and R-410A
Understanding how R-404A stacks up against other common refrigerants helps make sense of the bigger picture. Each refrigerant has its sweet spot, and knowing these differences prevents costly mistakes.
R-404A versus R-22 tells the story of the last major refrigerant transition. R-404A operates at higher pressures than R-22, which meant many retrofit installations needed pressure control adjustments. The oil compatibility difference is huge - R-404A requires POE oil while R-22 uses mineral oil. This oil change alone made simple drop-in conversions impossible.
From an environmental standpoint, both refrigerants have zero ozone depletion potential, but R-404A's higher GWP made it a temporary solution rather than a permanent fix. Refrigeration capacity typically improved with R-404A, especially in low-temperature applications where R-22 struggled to maintain efficiency.
R-404A versus R-410A represents two different evolutionary paths. R-410A operates at significantly higher pressures - we're talking about systems designed for 400+ psig versus R-404A's more moderate pressure ranges. The application split is clear: R-410A dominates air conditioning while R-404A rules refrigeration.
Both refrigerants require POE oil but different viscosity grades. Using the wrong oil viscosity causes lubrication problems and premature compressor failure. Environmental profiles show R-410A with lower GWP (2,088 vs 3,922), but both are now considered high-GWP refrigerants facing phase-down pressure.
System efficiency varies by application. R-410A typically achieves higher SEER ratings in air conditioning applications, while R-404A excels in the low-temperature refrigeration work we specialize in at American Mortuary Coolers.
Frequently Asked Questions about the R404 Chart
What are normal operating pressures for R-404A?
The pressures you'll see on your gauges depend a lot on what type of system you're working on and how hot it is outside. For walk-in coolers and other medium-temperature applications, you'll typically see suction pressures between 15-25 psig. This corresponds to evaporator temperatures around 0-10°F on the r404 chart.
When it comes to discharge pressures, expect to see 200-270 psig when the outdoor temperature is around 90°F. Hotter days mean higher head pressures - that's just physics working against you.
Freezer applications run quite a bit different. These low-temperature systems operate with suction pressures in the 5-15 psig range, which translates to evaporator temperatures of -10 to 0°F according to the r404 chart. The discharge pressures on freezers typically run 150-250 psig, depending on how hard the condenser is working.
At American Mortuary Coolers, we've seen these pressure patterns consistently across our installations from Tennessee to Georgia and beyond. The key is knowing what's normal for your specific application so you can spot problems before they become expensive repairs.
How do I measure superheat with the r404 chart?
Calculating superheat with the r404 chart is one of those fundamental skills that separates the pros from the newcomers. The good news is it's pretty straightforward once you get the hang of it.
Start by measuring the actual temperature at your evaporator outlet using a good calibrated thermometer. Don't rely on cheap gauges for this - accuracy matters when you're trying to dial in superheat.
Next, read your suction pressure and find the corresponding saturation temperature on the r404 chart. This is where the chart becomes your best friend - it tells you exactly what temperature that refrigerant should be at that pressure.
Finally, do the math: subtract the saturation temperature from your actual measured temperature. That difference is your superheat. For example, if your evaporator outlet reads 20°F and your suction pressure shows 32.6 psig (which equals 0°F saturation on the chart), you've got 20°F of superheat.
Most commercial refrigeration systems work best with 8-12°F of superheat, though some equipment has different requirements. Too little superheat means you might be flooding liquid back to the compressor. Too much suggests you're probably undercharged or have expansion valve issues.
Are there phase-out deadlines for R-404A?
This is the question that keeps a lot of technicians up at night, and for good reason. The EPA's AIM Act is phasing down HFC production to just 15% of baseline levels by 2036. That's a massive reduction that directly affects R-404A availability and pricing.
The tricky part is understanding the difference between "products" and "systems" in the regulations. Factory-built equipment faces earlier restrictions than field-assembled systems. Equipment manufacturers are already switching to lower-GWP alternatives to stay ahead of these deadlines.
Here's some good news though - existing R-404A systems can keep running and you can still service them with recovered or recycled refrigerant. The phase-down affects new production, not what's already in the field.
But let's be honest about the writing on the wall. Smart facility managers are already planning transitions to alternatives like R-448A or R-449A for long-term reliability and cost control. The sooner you start planning, the more options you'll have and the better deals you can negotiate.
At American Mortuary Coolers, we're helping our customers understand these changes and plan accordingly. Nobody wants to be caught off guard when their refrigerant becomes hard to find or expensive to buy.
Conclusion
The r404 chart has been your companion throughout this journey into commercial refrigeration mastery. After years of designing custom mortuary cooling systems here in Tennessee and shipping them nationwide, I've learned that technicians who truly understand pressure-temperature relationships are the ones who solve problems faster and build systems that last.
Think about it - every time you walk up to a refrigeration system with gauges in hand, you're about to have a conversation with that equipment. The r404 chart translates what the system is telling you through its pressures and temperatures. When the suction pressure reads 18 psig and you know that corresponds to about 5°F saturation temperature, you're no longer guessing - you're diagnosing with confidence.
The regulatory landscape is shifting beneath our feet, and R-404A won't be around forever in its current form. But here's the thing - the fundamental skills you've developed reading R-404A charts transfer beautifully to working with R-448A, R-449A, and whatever comes next. The pressure-temperature relationship concept remains constant, even as the specific numbers change.
At American Mortuary Coolers, we see this knowledge in action every day. Our custom mortuary coolers depend on precise temperature control - there's no room for guesswork when you're preserving someone's loved one. Whether we're shipping a unit to a funeral home in Georgia or installing a walk-in system in Illinois, that same r404 chart understanding ensures our equipment performs exactly as designed.
The beauty of mastering these fundamentals is how they compound over time. Today's superheat calculation becomes tomorrow's quick diagnostic check. This month's charging procedure becomes next year's training session for a newer technician. Knowledge shared is knowledge multiplied.
For deeper insights into pressure-temperature relationships and advanced diagnostic techniques, our Comprehensive Guide to 404A Pressure Temperature Charts offers additional resources to keep your skills sharp.

The r404 chart is more than just numbers on a page - it's your roadmap to reliable refrigeration. Keep it handy, use it often, and never stop learning. The industry needs skilled technicians who understand both the science and the art of keeping things cold.

















